Untold Herstories
We’ve all heard of history’s great kings, but what about the queens who shaped the world? The women on this list may have first gotten their power from the men around them but it would take equal parts ambition, intelligence, and ruthlessness to stay on the throne and leave their mark in the annals of history.
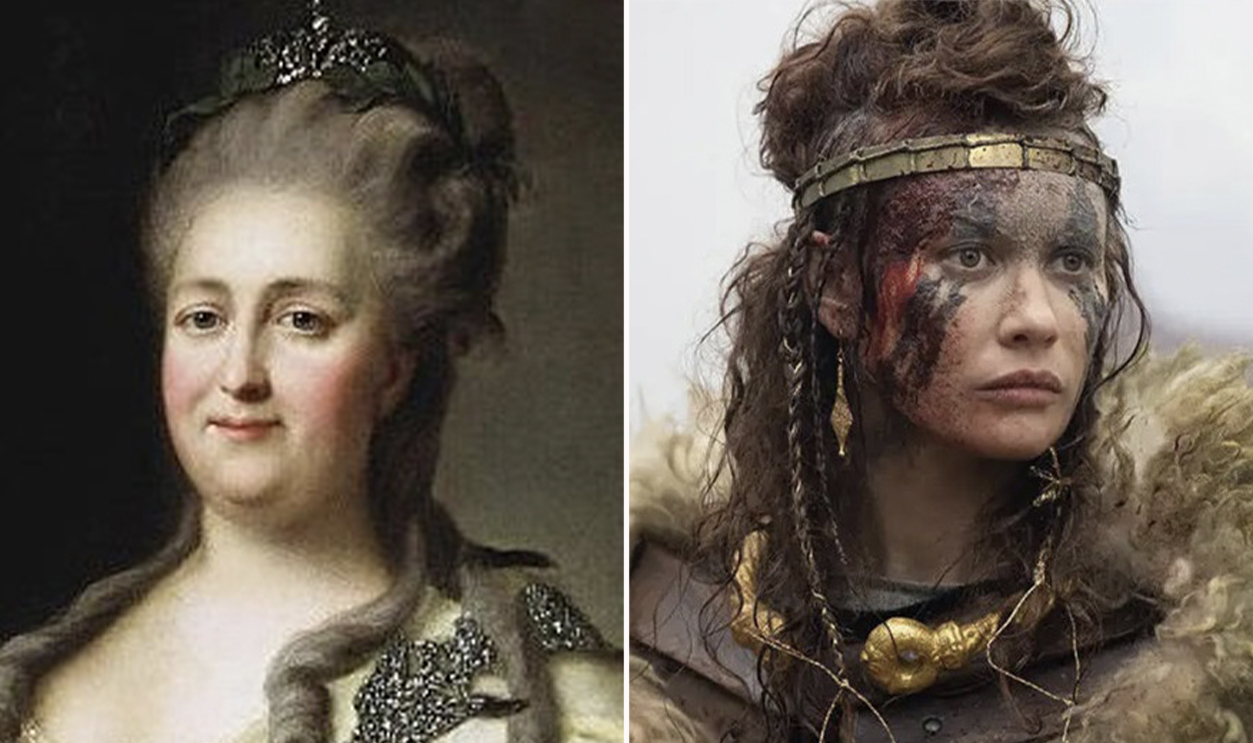

1. Boudica
Queen Boudica, leader of the ancient Iceni tribe, has become a legendary figure and symbol of justice. When Boudica’s husband passed on in 60 AD, the crown fell to her—but the Roman Empire had no respect for Iceni law and swept in to conquer the once-independent kingdom.
Boudica: A Humiliating Punishment
In a ruthless effort to break Boudica’s spirit, the Romans had the queen publicly flogged before assaulting her two daughters. But the Romans had underestimated Boudica, and these brutal acts only made her more determined to destroy them. She had been trained as a warrior, and before long, had gathered an army of British tribes to exact their vengeance on the Romans.
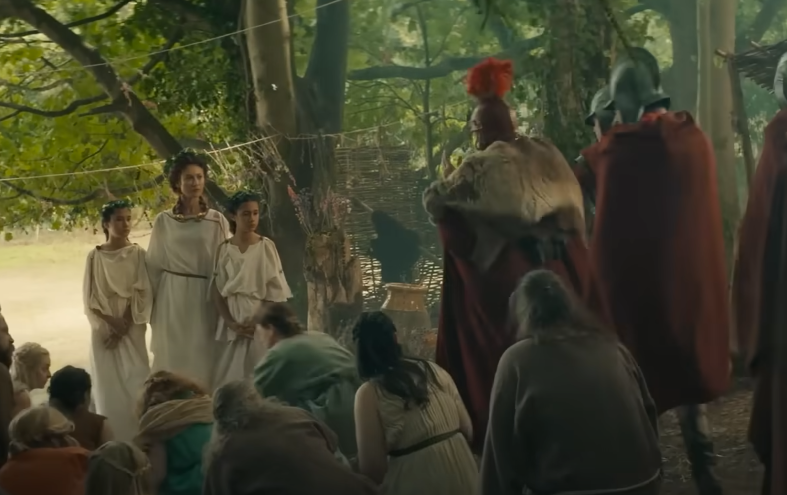 Bleiberg Entertainment, Boudica: Queen of War (2023)
Bleiberg Entertainment, Boudica: Queen of War (2023)
Boudica: Time For Revenge
Boudica’s army cut through three major Roman cities, including present-day London. She and her followers slew between 70,000 and 80,000 Romans and their Briton supporters. After the first two battles, it seemed that Boudica was destined for victory. But fate had other plans, and the final battle with the Romans was her last.
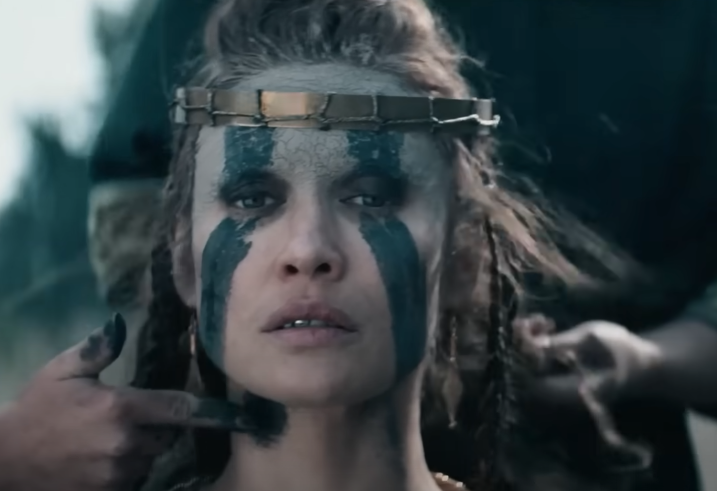 Bleiberg Entertainment, Boudica: Queen of War (2023)
Bleiberg Entertainment, Boudica: Queen of War (2023)
Boudica: How Did It End?
Historical records tell different accounts of Boudica’s demise. According to Tacitus, she took her own life, with poison. But Dio says she succumbed to sickness and was given a lavish burial. Modern historians have no evidence to support either theory, but also say that that the truth may be a combination of both accounts.
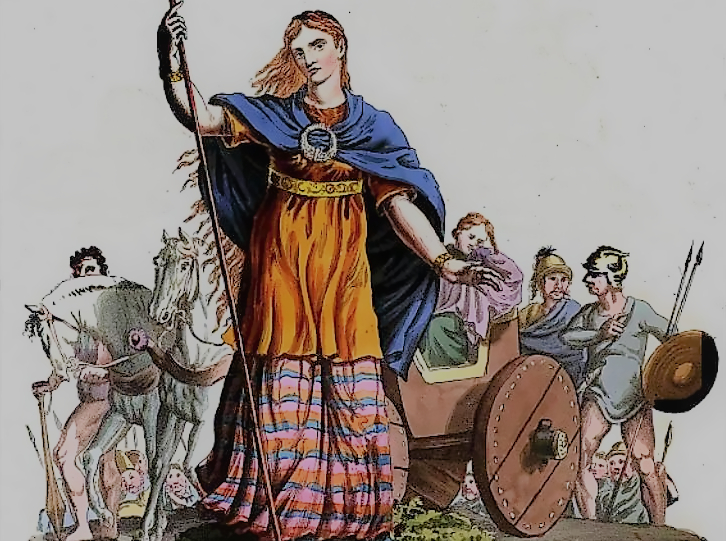 Charles Hamilton Smith, Wikimedia Commons
Charles Hamilton Smith, Wikimedia Commons
2. Wu Zetian
Empress Wu Zetian made history for being the first and only female empress of China.
She ruled for a total of 40 years—the first 25 were as a de facto ruler for her husband and sons, and the last 15 were as Empress in her own right. In a move that shocked the nation, she founded the Wu Zhou Dynasty to truly claim her power. Though it was short-lived, her dynasty was a time of great expansion for China.
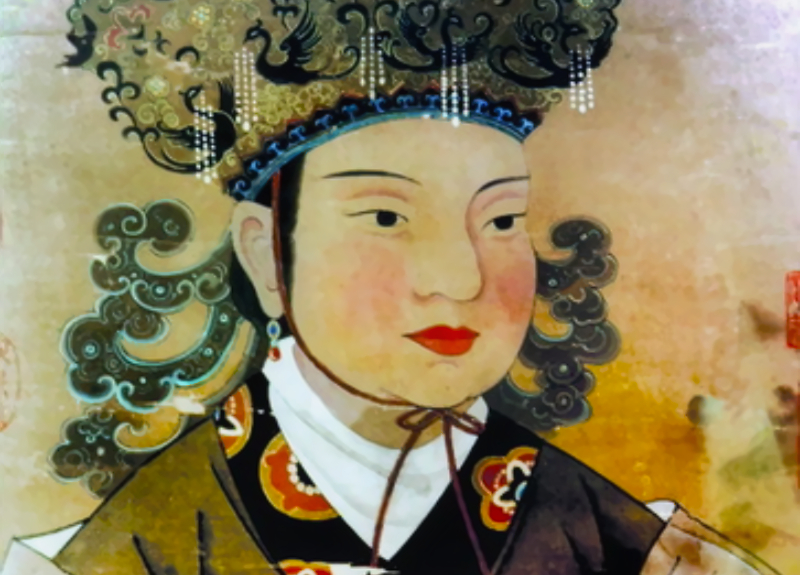 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Wu Zetian: A Friend To The People
Under her rule, China’s economy flourished, and she won over the peasant class by coming down hard on corruption within the government and truly listening to their concerns. She was also a strong supporter of the arts and literature and campaigned to improve the rights of women.
But it would take more than happy peasants to stay in power—Wu Zetian proved her might by conquering new lands in Korea and Central Asia, making China into one of the most powerful empires of the day.
 China Film Group Corporation, The Empress of China (2014)
China Film Group Corporation, The Empress of China (2014)
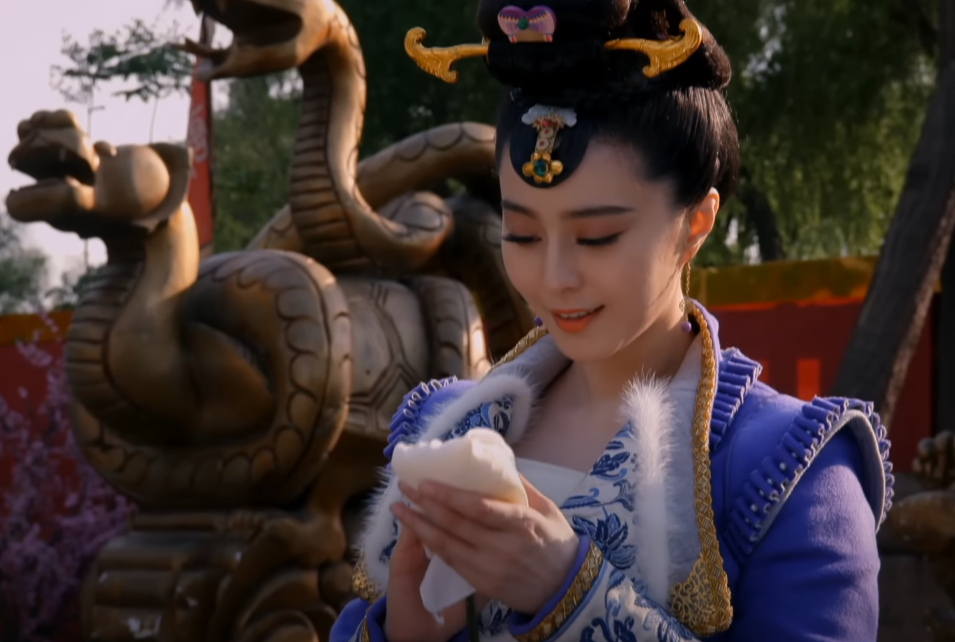
Wu Zetian: Humble Beginnings
Wu Zetian didn’t always have it so good—when she first arrived at the imperial court, it was a concubine to Emperor Taizong. When he died, she stayed close to the throne by marrying his son and successor, Emperor Gaozong.
It was during this time that the Empress was able to prove just how intelligent, charismatic, and ambitious she was. She was also more decisive than the Emperor, and before long, had become the true power behind the throne.
 China Film Group Corporation, The Empress of China (2014)
China Film Group Corporation, The Empress of China (2014)
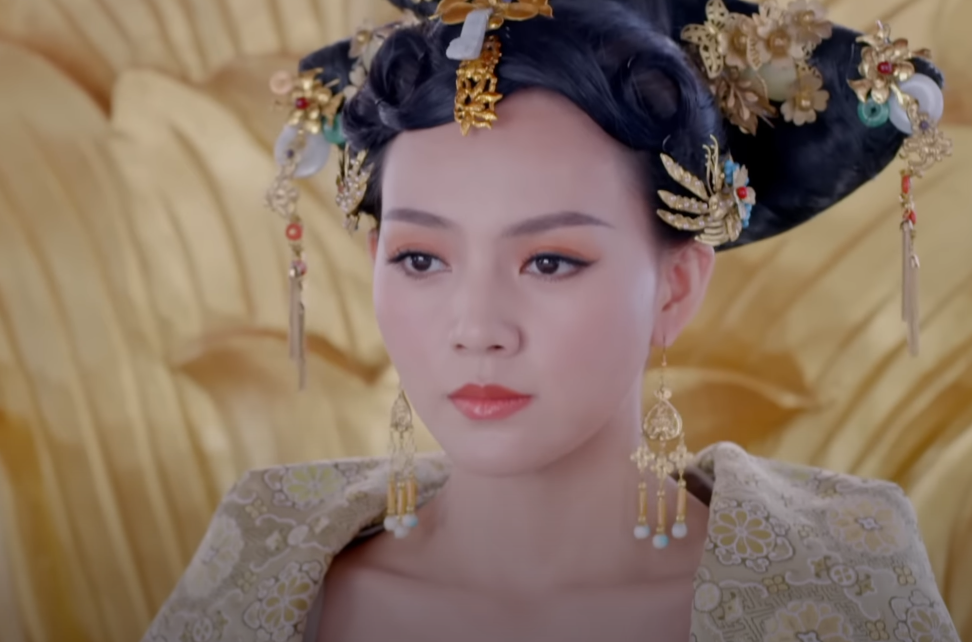
Wu Zetian: By Any Means Necessary
The Empress was ruthless when it came to holding on to her power.
She created a network of spies to monitor—and eliminate—any real or imagined rivals. Those who crossed her were often exiled with their families, and she was just as cold-hearted when it came time to dealing with her own folks. After a relative tried to oust her from power, she retaliated by slaying 12 branches of the imperial family, just for being associated with the traitors.
 China Film Group Corporation, The Empress of China (2014)
China Film Group Corporation, The Empress of China (2014)
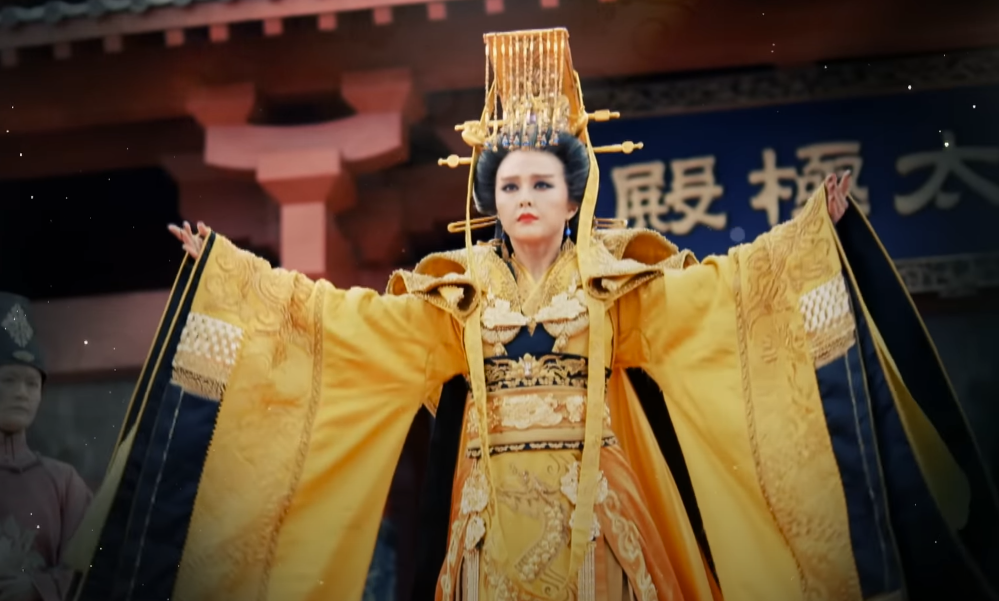
Wu Zetian: Clinging To The Throne
When Wu Zetian’s son came into power, she refused to give up her authority. As the Empress regent, she was able to block him from getting involved in affairs of state.
In 690, Wu Zetian got tired of being polite about things and forced her son, Emperor Ruizong, to abdicate the throne.
 China Film Group Corporation, The Empress of China (2014)
China Film Group Corporation, The Empress of China (2014)
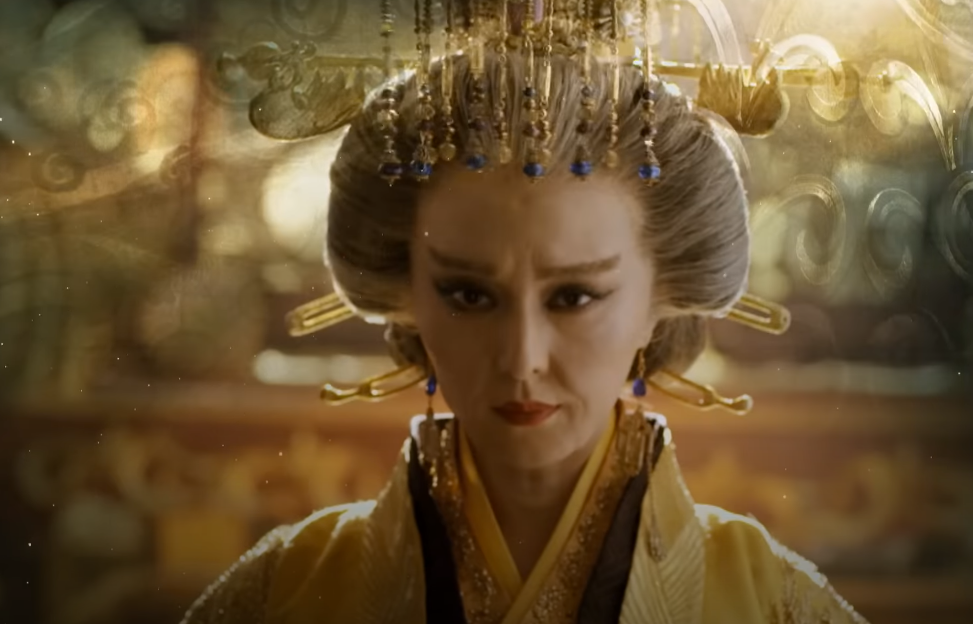
Wu Zetian: The Bitter End
With her son out of the way, the Empress named herself the sole ruler of China and founded the Wu Zhou Dynasty, which thrived for the next 15 years.
Wu Zetian finally met her match in 705, when she was ousted from power by a coup. She perished later that year.
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
3. Hatshepsut
Queen Hatshepsut took on the mantle of Pharaoh during Egypt’s 18th Dynasty, and brought peace, prosperity, and architectural innovation to her people throughout her 22-year reign. Born the eldest daughter of Pharaoh Thutmose I and Queen Ahmose, Hatshepsut was about 14-years old when she married her half-brother, Thutmose II.
But it was through her stepson/nephew that she would gain Egypt’s throne.
 Metropolitan Museum of Art, Wikimedia Commons
Metropolitan Museum of Art, Wikimedia Commons
Hatshepsut: Taking The Throne
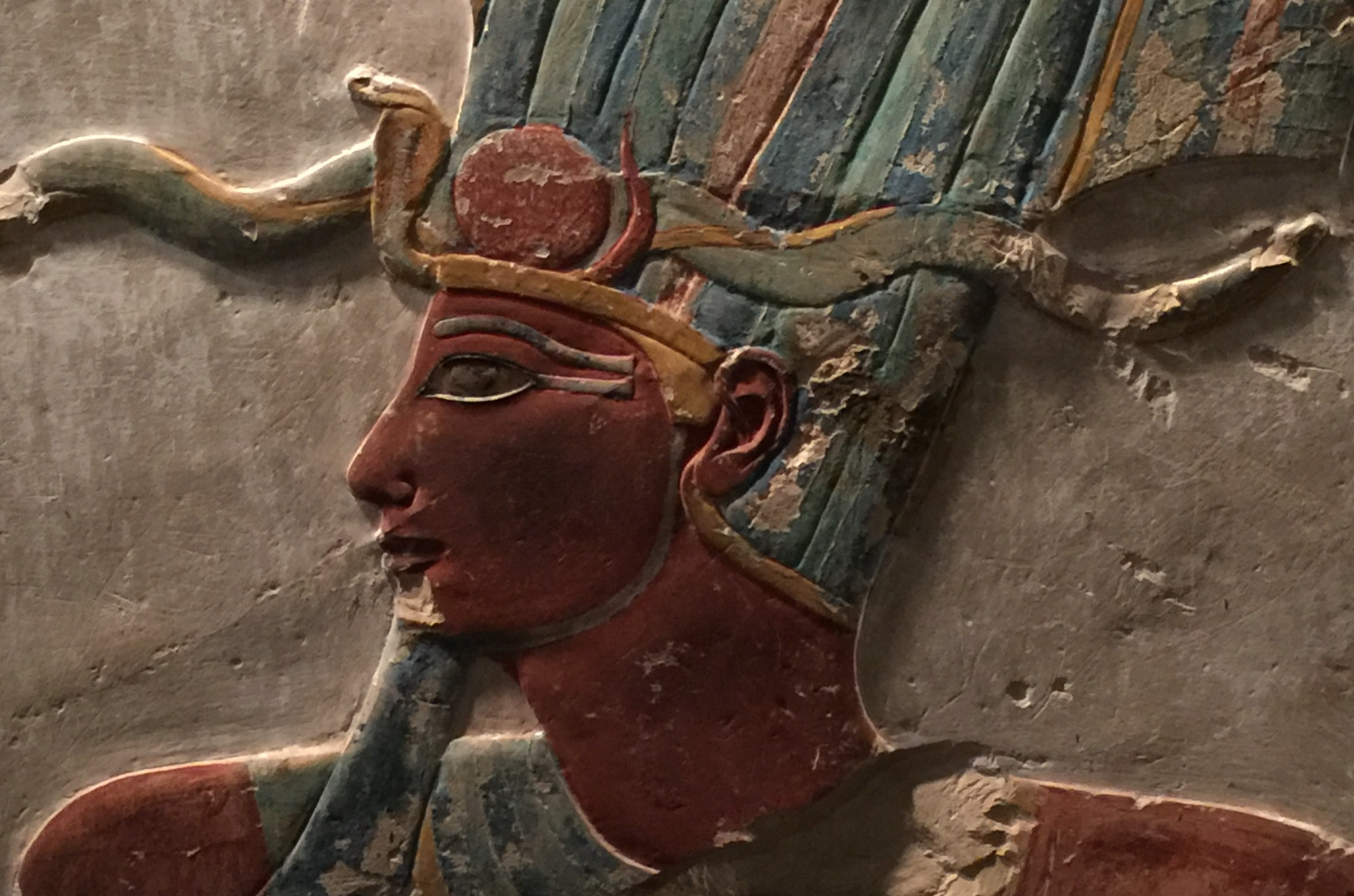
Hatshepsut’s stepson and nephew, Thutmose III, was only two years old when he inherited the kingship, so she became the queen regent. But in 1478 BCE, Hatshepsut took on the title of Pharaoh and became a co-ruler with the boy king.
It was the first time a woman had ever been crowned Pharaoh, but if she wanted to keep the throne, she would have to change her image.
 EditorfromMars, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
EditorfromMars, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Hatshepsut: A New Look
Like many ancient societies, Egypt was very patriarchal. To secure her position as Pharaoh, Hatshepsut took on a masculine appearance, wearing a fake beard and traditional kilts for men. In artwork, she was portrayed with big muscles, and in more violent reliefs that would have been typical of male pharaohs, like an image of her smashing the heads of prisoners.
 Black Plus Plus Productions, Hatshepsut (2019)
Black Plus Plus Productions, Hatshepsut (2019)
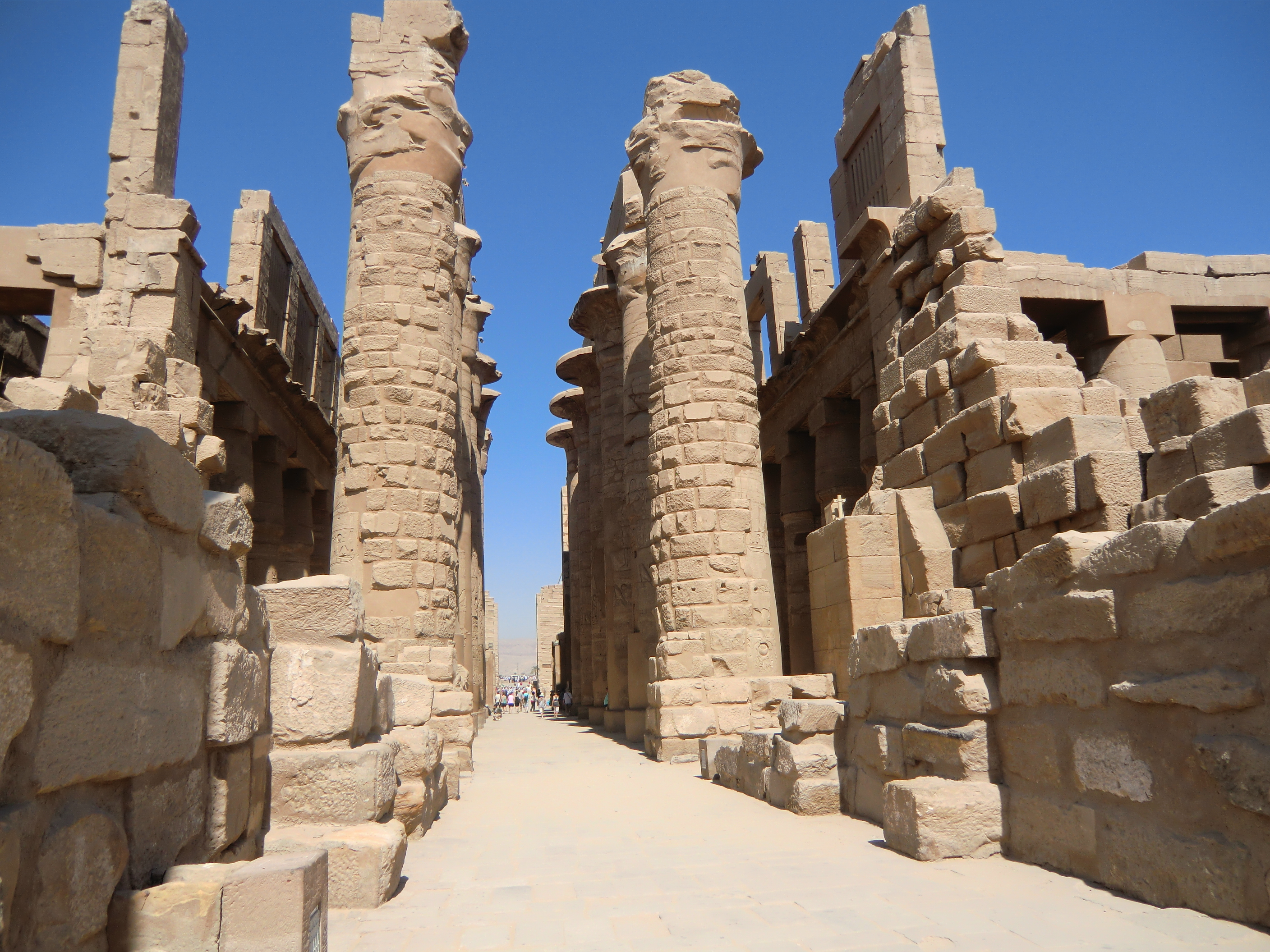
Hatshepsut: The Great Builder
Hatshepsut's reign was a period of growth for Egypt and she oversaw the construction of several building projects. Some of her more notable construction projects include restoration work at the Karnak Temple Complex, the Red Temple, and the Mortuary Temple of Hatshepsut at Deir el-Bahari.
 René Hourdry, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
René Hourdry, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Hatshepsut: Erased From History
Hatshepsut was almost forgotten by history as, after her death, Pharoah Thutmose III scrubbed her name from public records.
He also destroyed statues of Hatshepsut and carved her image out of many public monuments. Thutmose III and several of the pharaohs after him took credit for Hatshepsut’s accomplishments—luckily, the world started to learn the truth when Egyptologists discovered hieroglyphs in Deir el-Bahari temple that depicted the forgotten female pharaoh.
 Hedwig Storch, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
Hedwig Storch, CC BY-SA 3.0, Wikimedia Commons
4. Tomyris Of The Massagetae
Tomyris, Queen of the Massagetae, cemented her place in history when she bravely stood against the Persian King Cyrus the Great.
Tomyris succeeded to the throne after the passing of her husband, but it wasn’t long before another man came looking to make her a wife again. As the story goes, Cyrus got mad when Tomyris turned down his offer of marriage, so he retaliated by invading her lands.
 Andrea del Castagno, Wikimedia Commons
Andrea del Castagno, Wikimedia Commons
Tomyris Of The Massagetae: Tragedy Strikes
Tomyris’ son, Spargapises, led the Massagetae army in the battle against Cyrus’ army. Unfortunately, Spargapises and his soldiers went into battle having had one too many drinks.
In their drunken state, they were easily defeated, and Cyrus himself executed Spargapises.
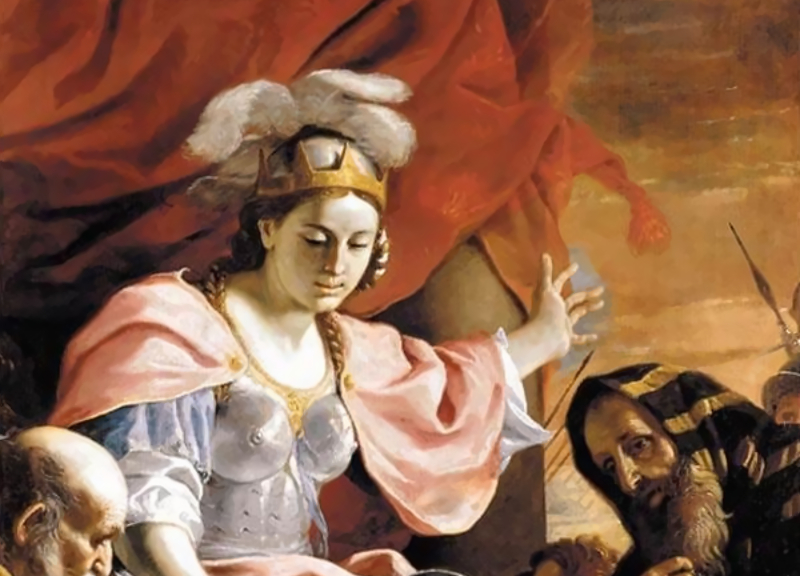
Tomyris Of The Massagetae: Bloody Vengeance
Tomyris vowed to get revenge and led her army to battle against the great king. To everyone’s surprise, she emerged victorious. Reportedly, she put Cyrus’ severed head in a bowl filled with blood and said: “There:
Drink your fill of blood"! After the battle, Tomyris vanished from the historical record.
 Mattia Preti, Wikimedia Commons
Mattia Preti, Wikimedia Commons
5. Zenobia Of Palmyra
When her husband, King Odaenathus, was assassinated, Queen Zenobia became regent to her son. She was the true power throughout his reign and made history when she declared Palmyra’s independence from the Roman Empire. She went on to expand her territories and, in 270 AD, she turned her eye toward the Romans.
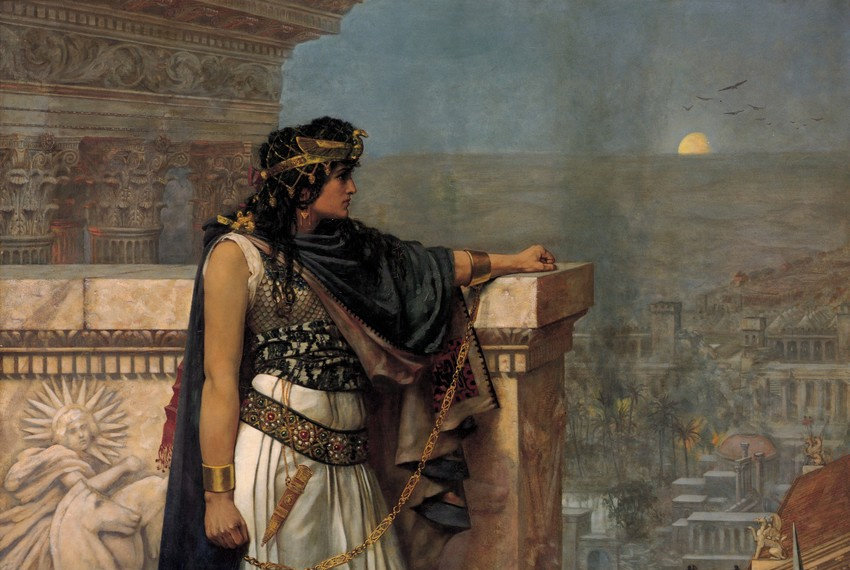 Herbert Gustave Schmalz, Wikimedia Commons
Herbert Gustave Schmalz, Wikimedia Commons
Zenobia Of Palmyra: The Conqueror
In 270 AD, Zenobia launched a campaign that would see her conquer most of the Roman East. In addition to her army campaign, Zenobia was a respected leader for her promotion of cultural and religious tolerance. While she came to be seen as a powerful symbol of rebellion against imperial oppression, her luck ran out just a couple of years after her great campaign.
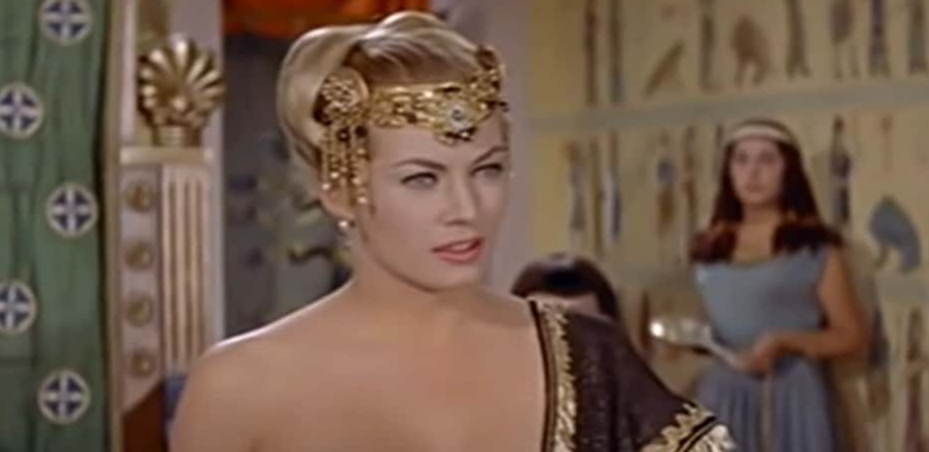 Glomer Film, Sign of the Gladiator (1959)
Glomer Film, Sign of the Gladiator (1959)
Zenobia Of Palmyra: The Emperor Steps In
In 272, Emperor Aurelian went on the march to quell Zenobia’s rebellion. After much fighting, the queen found herself on the losing end, with her city under siege. In the end, she was captured by Aurelian and taken to Rome. Historians still debate on whether Zenobia was executed after Aurelian’s triumph in 274 or if he allowed her to live out her remaining days in Tibur, with her children.
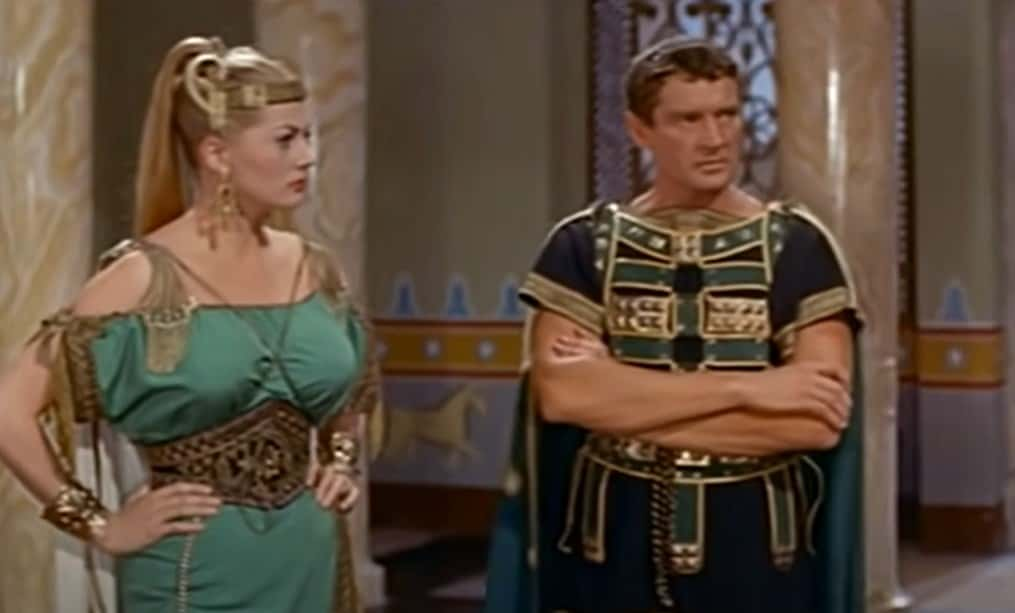 Glomer Film, Sign of the Gladiator (1959)
Glomer Film, Sign of the Gladiator (1959)
6. Queen Seondeok
Born Princess Deokman, the woman who would become Queen Seondeok knew she was destined to rule Korea.
Her father, King Jinpyeong of Silla, had no male heirs, so the princess asked if she could compete to prove that she was worthy of inheriting the throne, rather than it going to her brother-in-law. She won that competition, but that didn’t mean her reign was secure.
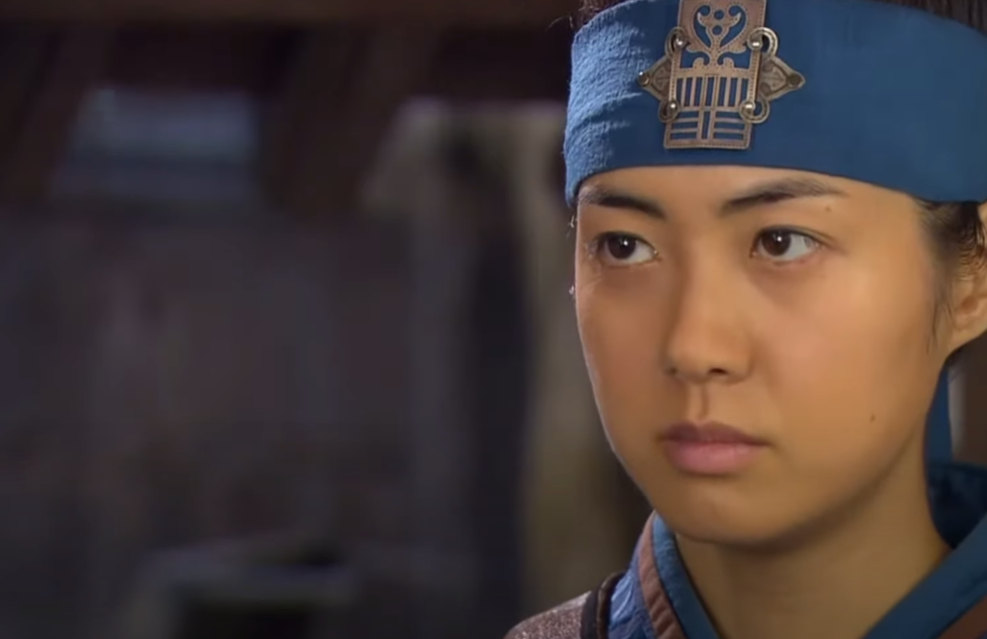 MBC, The Great Queen Seondeok (TV Series 2009)
MBC, The Great Queen Seondeok (TV Series 2009)
Queen Seondeok: Harsh Punishment
Although Silla, a kingdom in the Korean peninsula, had been ruled by a woman before, the concept still enraged many among the nobility. In 631 AD, two courtiers came up with a plan to disrupt Seondeok’s coronation with an uprising. Unfortunately for them, the Queen caught wind of the plot and had the traitors and their families publicly executed.
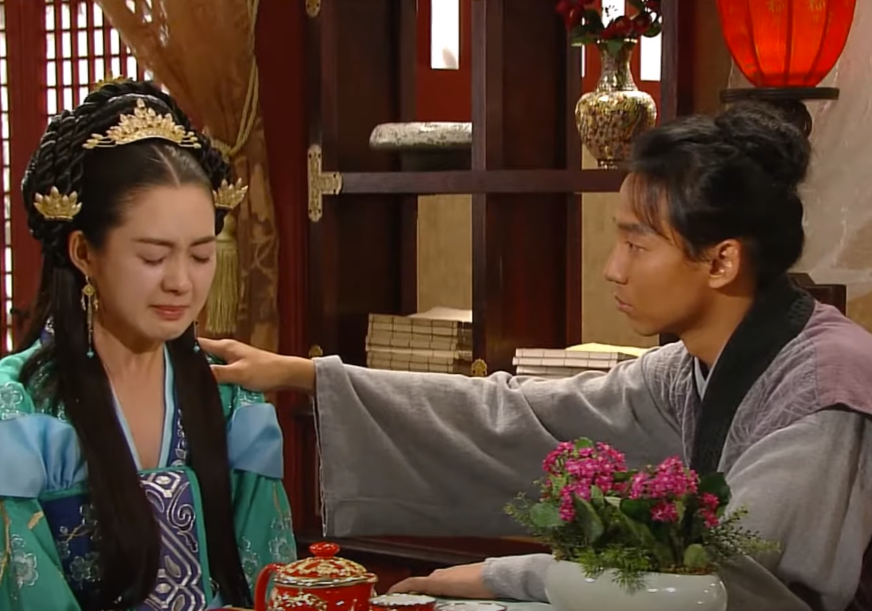 MBC, The Great Queen Seondeok (TV Series 2009)
MBC, The Great Queen Seondeok (TV Series 2009)
Queen Seondeok: A Real Queen
January 632 marked the start of Queen Seondeok’s 15-year reign. Unlike the other women who had ruled before her, she was Silla’s first true queen, not a regent or queen dowager. And while Silla and the other two Korean kingdoms were constantly instigating wars with each other, Seondeok ushered in a time of revival for Korean arts and culture.
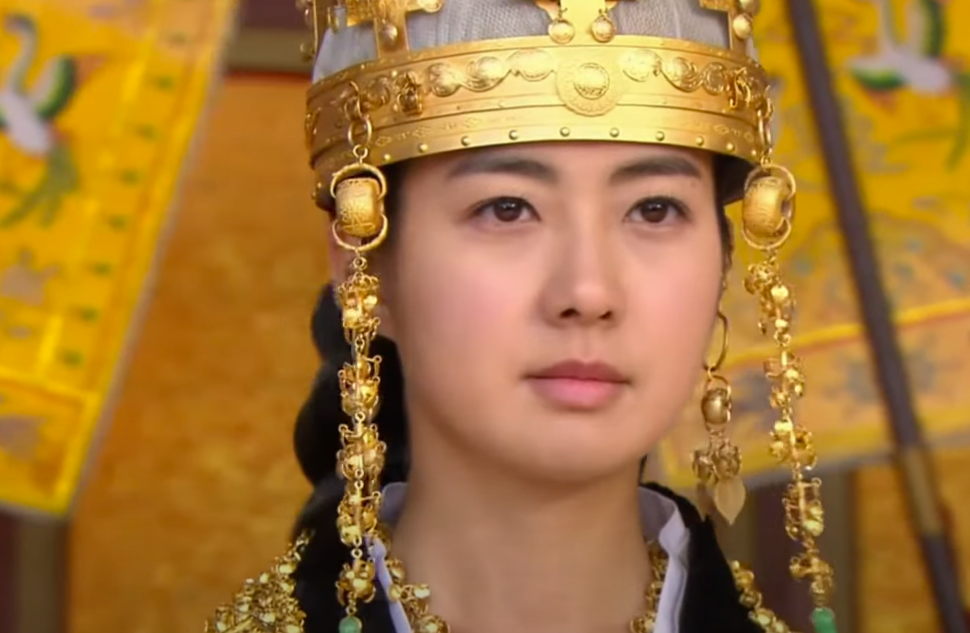 MBC, The Great Queen Seondeok (TV Series 2009)
MBC, The Great Queen Seondeok (TV Series 2009)
Queen Seondeok: She Cared For The People
Queen Seondeok was deeply concerned with her people’s wellbeing, and had royal inspectors work hard to improve the care of orphans, widows, the poor, and the elderly. She temporarily exempted peasants from paying taxes, and reduced taxes for Silla’s middle class. She also built Cheomseongdae, Asia’s oldest remaining astronomical observatory.
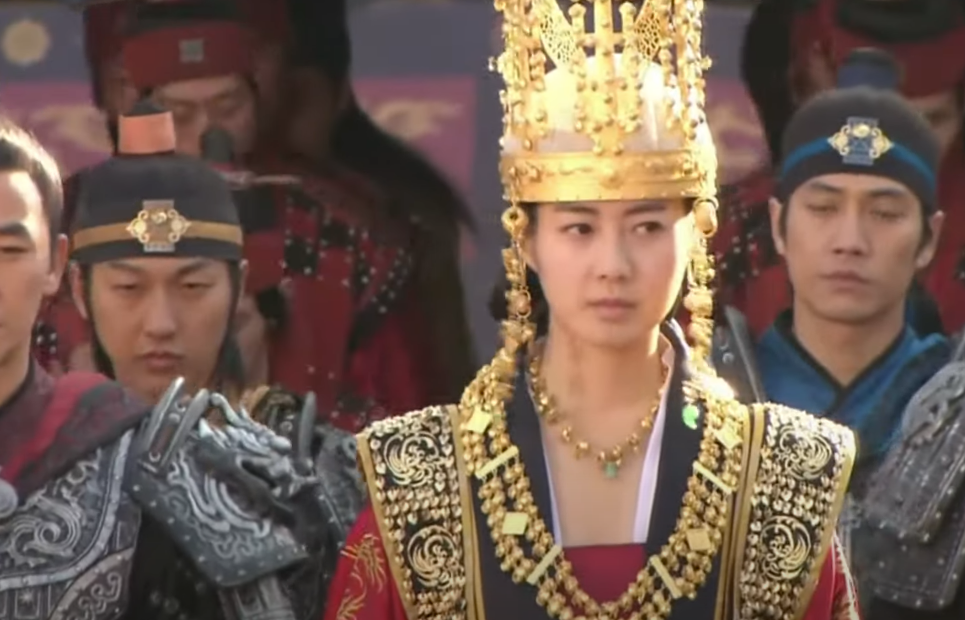 MBC, The Great Queen Seondeok (TV Series 2009)
MBC, The Great Queen Seondeok (TV Series 2009)
Queen Seondeok: She Was Betrayed
Seondeok dreamed of a day when Korea would be unified under Silla’s flag—but that day would never come. In 647, one of the Queen’s trusted advisers rebelled against her. The revolt only last ten days, but at the end of it, Queen Seondeok fell ill and perished.
Her cousin, Queen Jindeok, inherited the throne.
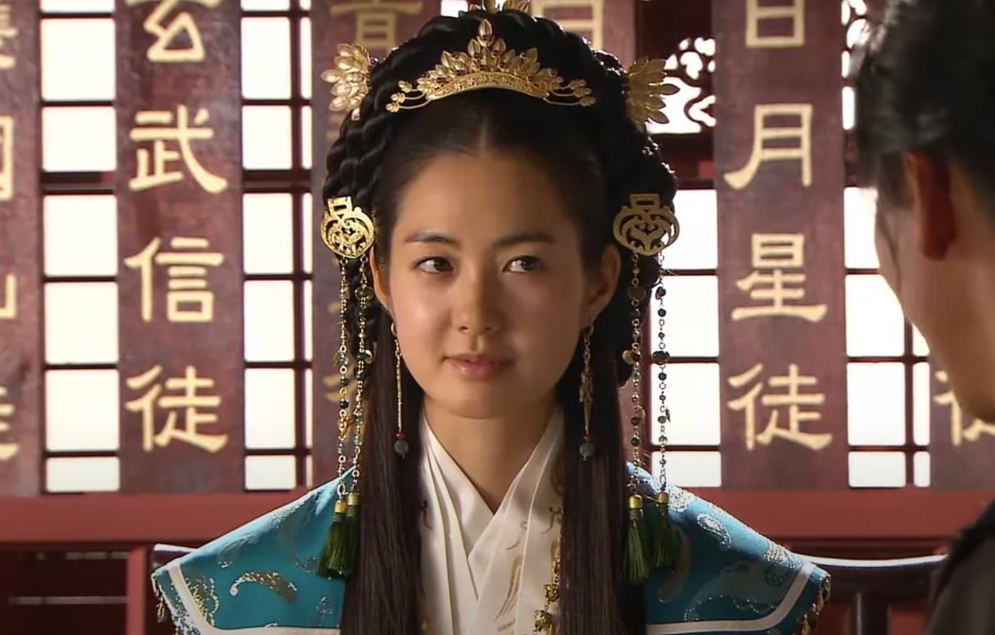 MBC, The Great Queen Seondeok (TV Series 2009)
MBC, The Great Queen Seondeok (TV Series 2009)
7. Artemisia I Of Caria
Artemisia I of Caria ruled over the Greek city-state of Halicarnassus, but today she remember as a fearless navy commander rather than a queen. Artemisia inherited the throne from her husband, and during the Greco-Persian Wars, her tactics and strategies would influence the outcome of crucial skirmishes, like the Battle of Salamis.
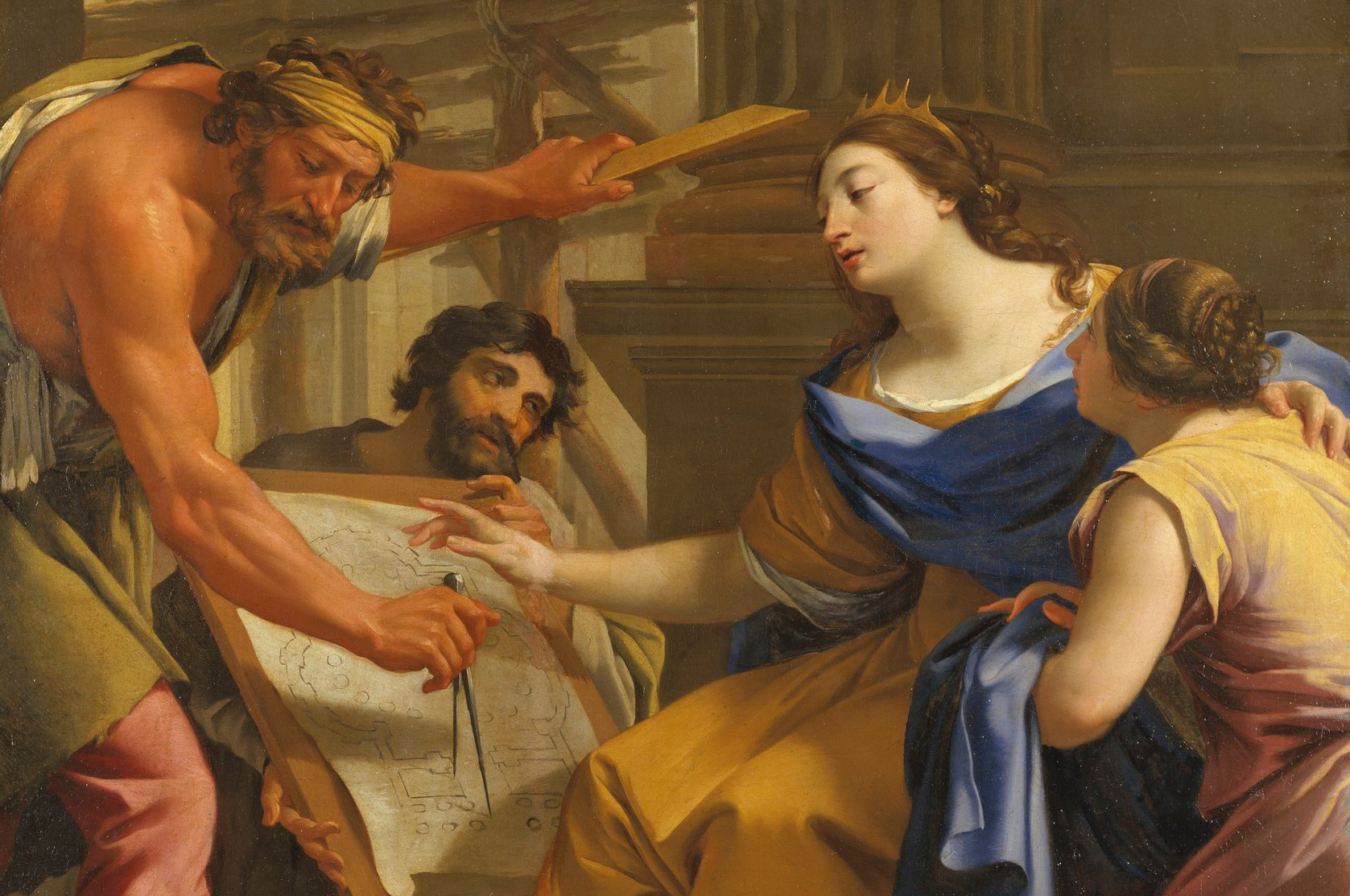 Simon Vouet, Wikimedia Commons
Simon Vouet, Wikimedia Commons
Artemisia I Of Caria: High Praise
The Persian King Xerxes praised Artemisia's battle prowess after the Battle of Salamis and gifted her a suit of Greek armor in honor of her bravery. Some reports even say that Xerxes she was so trusted by Xerxes, that he sent her to look after his illegitimate sons in Ephesus.
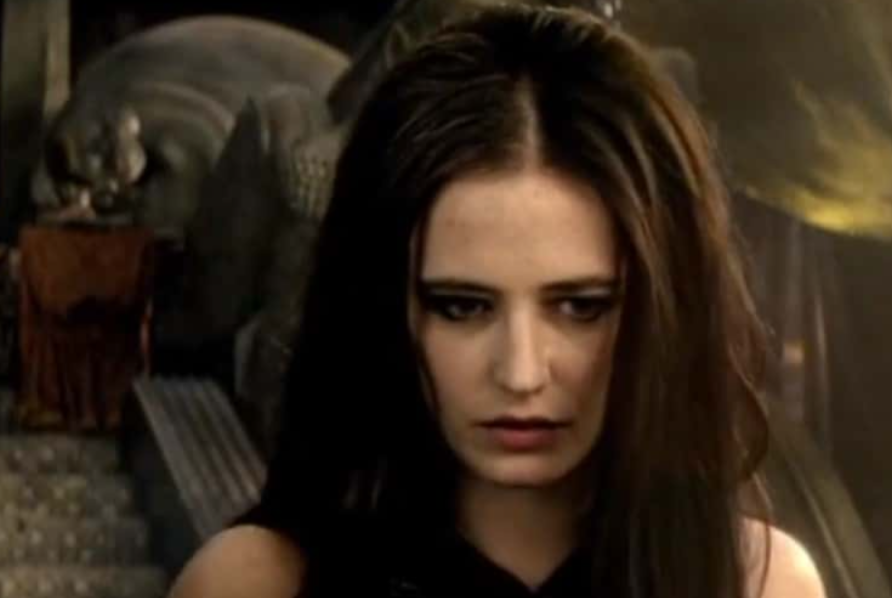 Warner Bros., 300: Rise of an Empire (2014)
Warner Bros., 300: Rise of an Empire (2014)
Artemisia I Of Caria: A Heartbreaking End
While her life was full of glory, the same cannot be said of Artemisia's passing. According to legends, she later met her end after going mad with love for a man named Dardanus. An oracle told her that the lovesickness could be cured by jumping from a cliff—Artemisia, to her doom, believed the oracle.
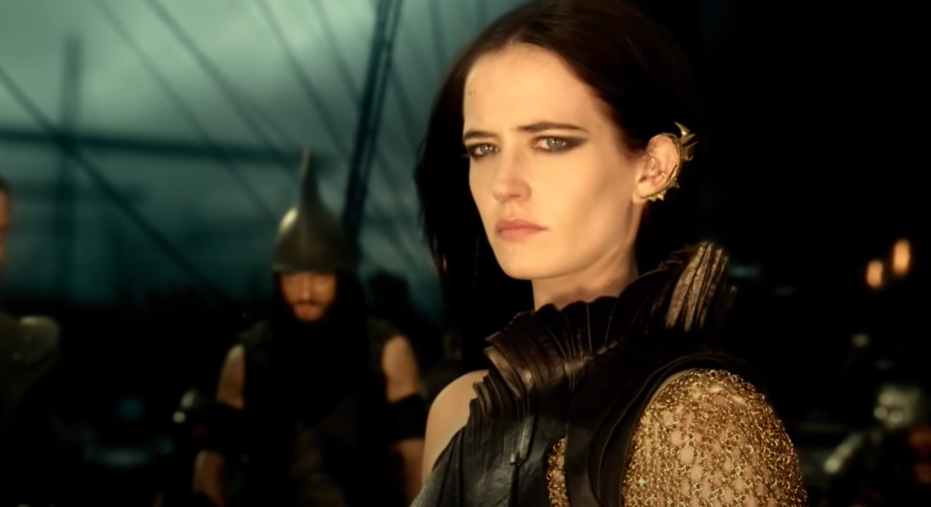 Warner Bros., 300: Rise of an Empire (2014)
Warner Bros., 300: Rise of an Empire (2014)
8. Cleopatra I Of Syra
Before the infamous Cleopatra we all know of, there was Cleopatra I, who rose to power through her marriage to King Ptolemy V of Egypt.
Cleopatra was a Seleucid princess and her marriage to Ptolemy had brought peace between the two nations. But that all hung in the balance when her husband passed on suddenly.
 NYPL, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
NYPL, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Cleopatra I Of Syra: Secret Plans
After the passing of her husband, Cleopatra’s son Plotemy VI became king. But the boy was only six years old, so his mother was named co-regent.
She was the first Ptolemaic queen to rule the country without a husband—but she’d ascended the throne at a time of great instability. Turns out that before his death, her husband had been planning to invade the Seleucid kingdom.
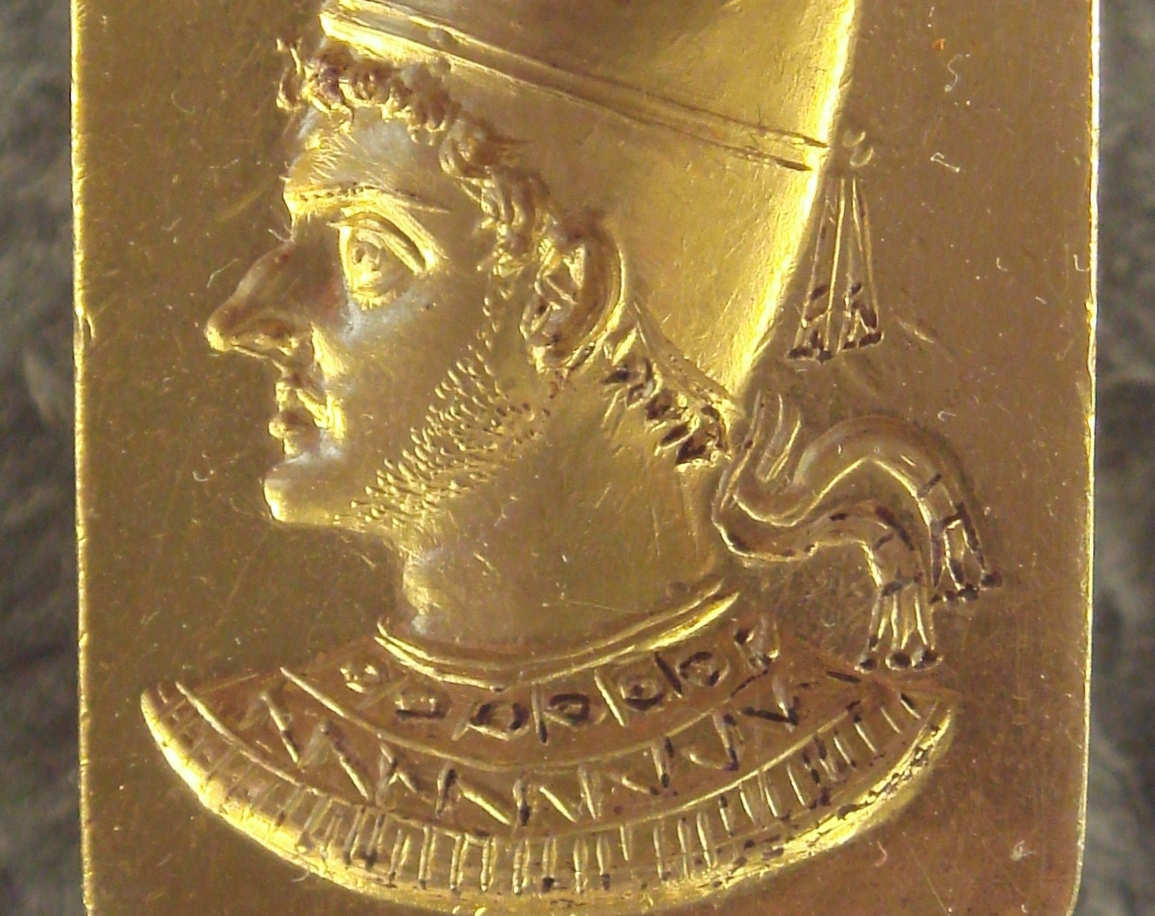 Louvre Museum, Wikimedia Commons
Louvre Museum, Wikimedia Commons
Cleopatra I Of Syra: She Made Peace
Instead of going to war, Cleopatra called for peace.
This act, along with her skills in diplomacy, led her to be seen as a stabilizing force in the world. Through her political alliances, Egypt’s influence expanded in Syria. Her kingdom prospered throughout her 16-year reign, but fell into conflict with the Seleucid Empire after she passed on.
9. Samsi Of Assyria
Queen Samsi came from a culture that was ruled by queen’s, and she took the throne when the former Arabian queen Zabibe abdicated. When the queen gave up the throne, she made Samsi swear to be loyal to the Assyrian king Tiglath-Pileser III. Tiglath-Pileser III had taken control of all the Arab nations, and while Samsi swore her fealty to him, she quickly changed her mind stoked the fires of rebellion.
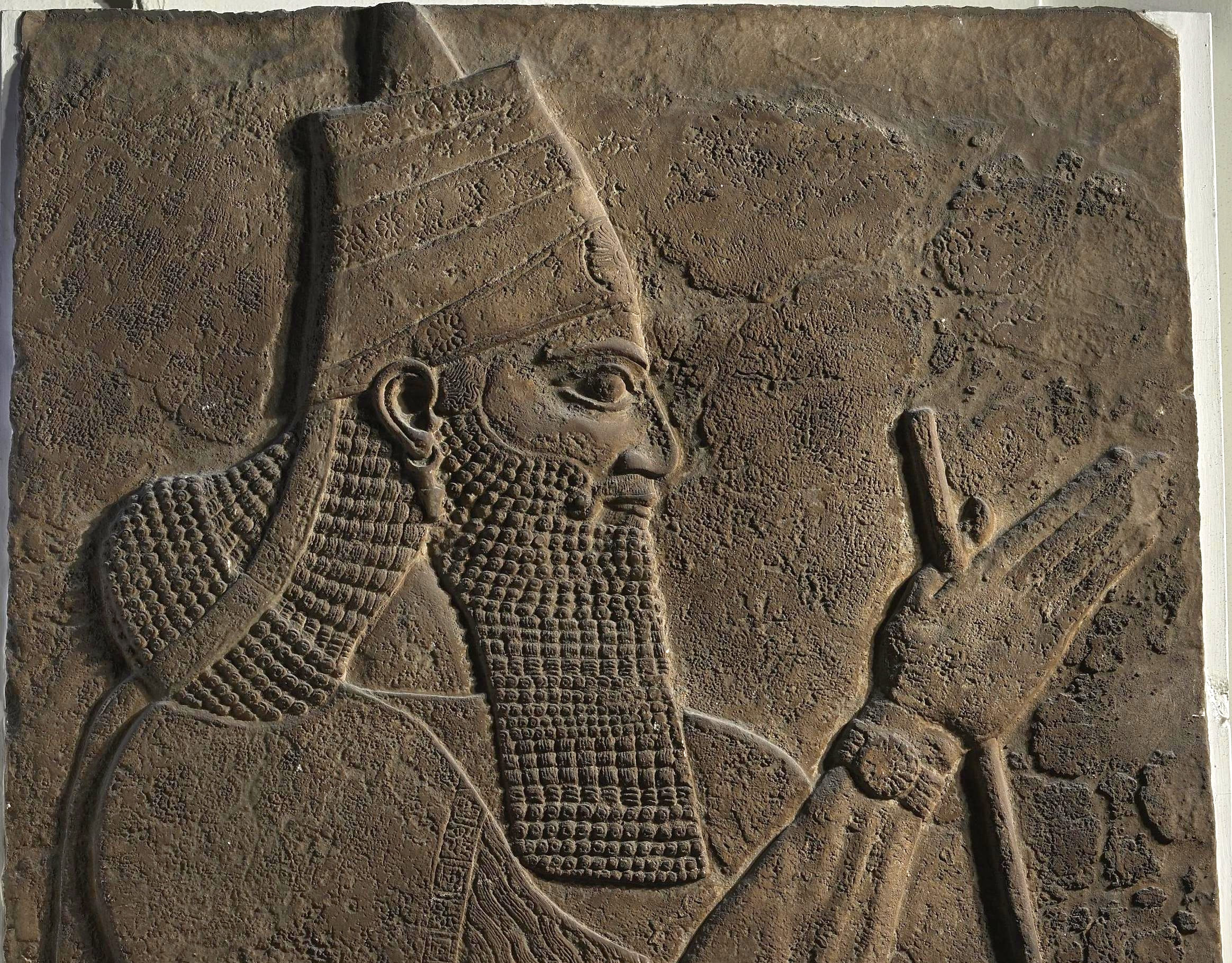 British Museum, Wikimedia Commons
British Museum, Wikimedia Commons
Samsi Of Assyria: A Brutal Defeat
Samsi joined forces with King Rezin of Damascus and together they brought the fight to Tiglath-Pileser III.
But the Assyrian king had the power of the world behind him, and in 732, the Assyrians defeated Samsi’s army. Thousands were killed while thousands more were taken as prisoners. Tiglath-Pileser III seized Samsi’s estate and burned all her tents near the battlefield. Samsi ran from the destruction, but her freedom was short-lived.
Samsi Of Assyria: A Twist Of Fate
Samsi was quickly captured and brought before the great Assyrian king. As luck would have it, Tiglath-Pileser III didn’t want her life—he wanted her to rule. The king needed an Arab ruler under his thumb, so he could keep order along the trade route from Assyria to Arabia.
Samsi would have to pay tribute to him and be monitored by a governor and 10,000 soldiers loyal to the king, but Tiglath-Pileser III restored her crown.
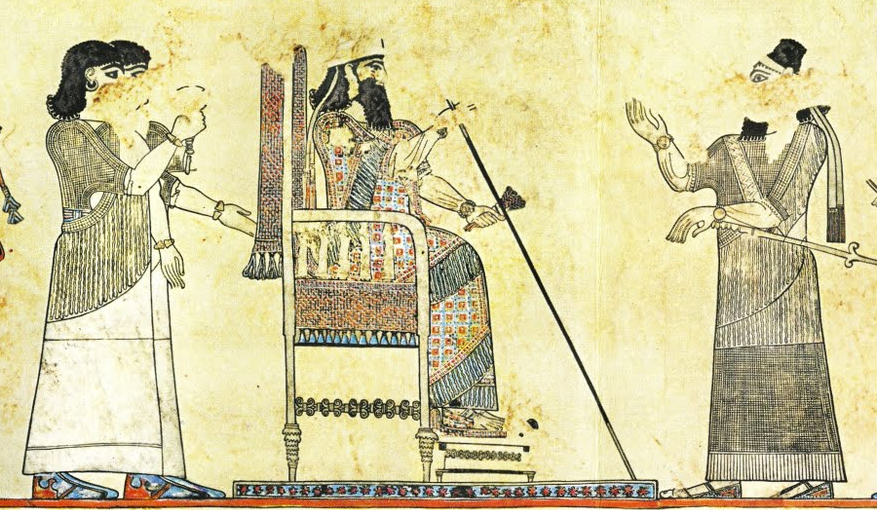 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
10. Cleopatra
Alongside two of her brothers, Cleopatra VII (yes, that Cleopatra) ruled Egypt for 21 years. She was the last true Egyptian ruler before Rome took over in 30 BCE. She was also the last member of the Ptolemaic Dynasty, which traced its origins to Macedon and Alexander the Great.
But while all that is historic enough, it was Cleopatra’s romantic entanglements that made her infamous.
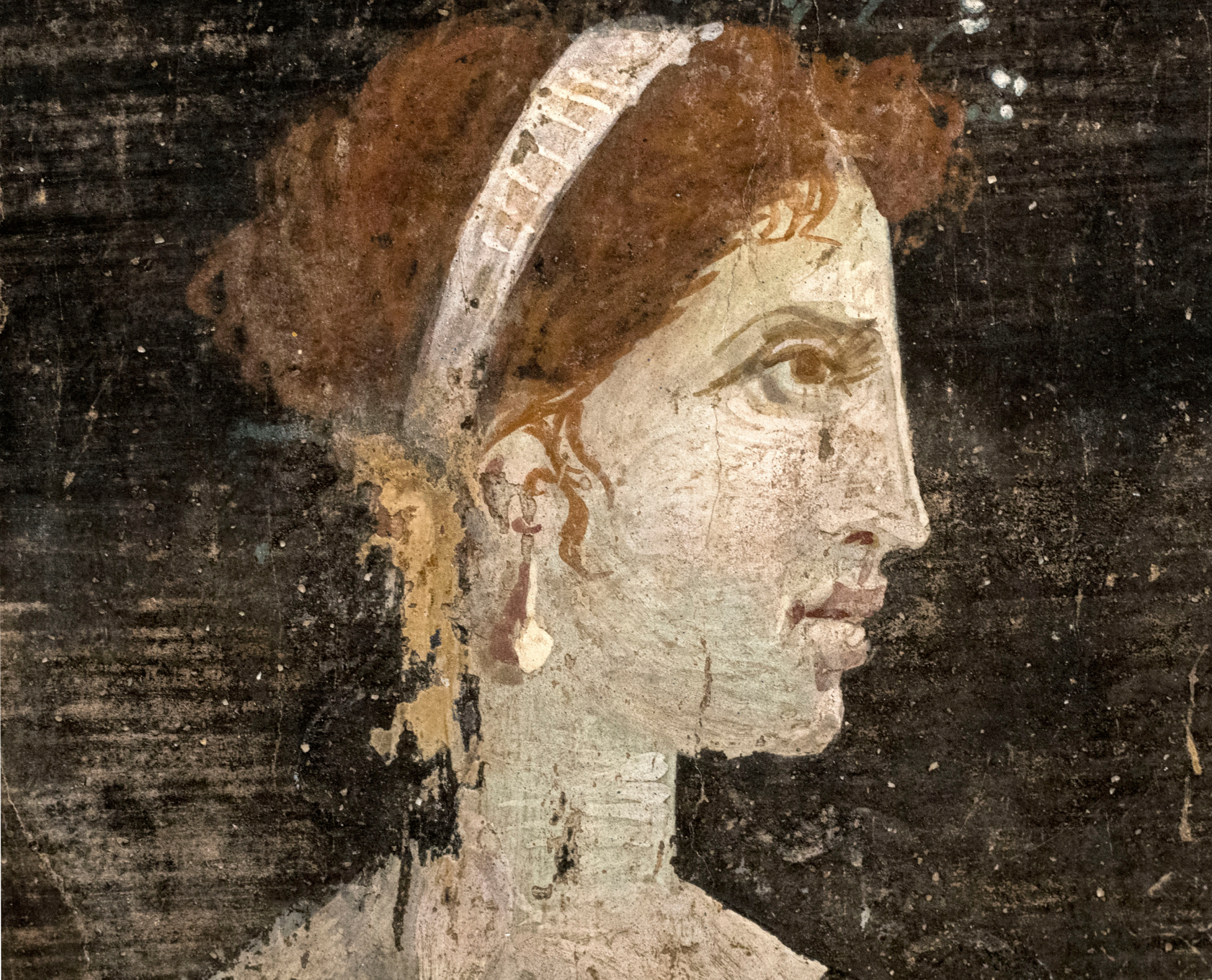 Ángel M. Felicísimo, Wikimedia Commons
Ángel M. Felicísimo, Wikimedia Commons
Cleopatra: Powerful Lovers
Cleopatra’s steamy liaisons are well known—first she hooked up with Julius Caesar and then she moved on to Marc Antony. And while her relationship with the latter has made for one of the world’s most beloved love stories, her main reason for wanting both men was that they made for powerful allies. When her father died in 51 BCE, Cleopatra and her brother Ptolemy XIII became co-rulers, but it didn’t take long for them to start fighting for full control of the throne.
 Lawrence Alma-Tadema, Wikimedia Commons
Lawrence Alma-Tadema, Wikimedia Commons
Cleopatra: She Won
Rome had been keeping an eye on the tensions in Egypt and Julius Caesar decided to take Cleopatra's side in the conflict. The two also became lovers, and Ptolemy XIII eventually met his end in battle.
But that didn’t mean Cleopatra had the throne all to herself yet. Caesar named her co-ruler, along with her brother Ptolemy XIV. Luckily for her, Ptolemy XIV perished in 44 BCE, the same year that Caesar was assassinated.
Cleopatra: A New Alliance
Once Caesar was out of the picture, Cleopatra solidified her rule by naming her and Caesar's son, Caesarion, as her co-ruler.
She then made an alliance with Marc Antony, who had been one of Caesar’s highest-ranking officers. The two got married, had twins, and enjoyed a time of bliss and political intrigue…but we all know it was doomed to a tragic end.
Cleopatra: A Legendary End
While Marc Antony was away fighting Octavian, the future Emperor Augustus, he received false word that Cleopatra had perished.
In despair, Antony fell on his sword. Cleopatra, refusing to be dragged back to Rome to be paraded in a triumph, took her own life. According to the legend, she let a poisonous snake bite her, bringing an end to the last ancient Egyptian dynasty.
 Angelica Kauffmann, Wikimedia Commons
Angelica Kauffmann, Wikimedia Commons














