The First Rulers Of Kingdoms And Empires
Did you know that the word "kingdom" originates from the Olde English word "cyning", which means "king" or "ruler"? Today, there are 43 monarchies worldwide and no officially recognized empires—the last of which was the British Empire, which ceased to be an empire after the Second World War and officially came to a conclusion after the Handover of Hong Kong to China in 1997. Let's examine with whom some of the greatest empires in history began.

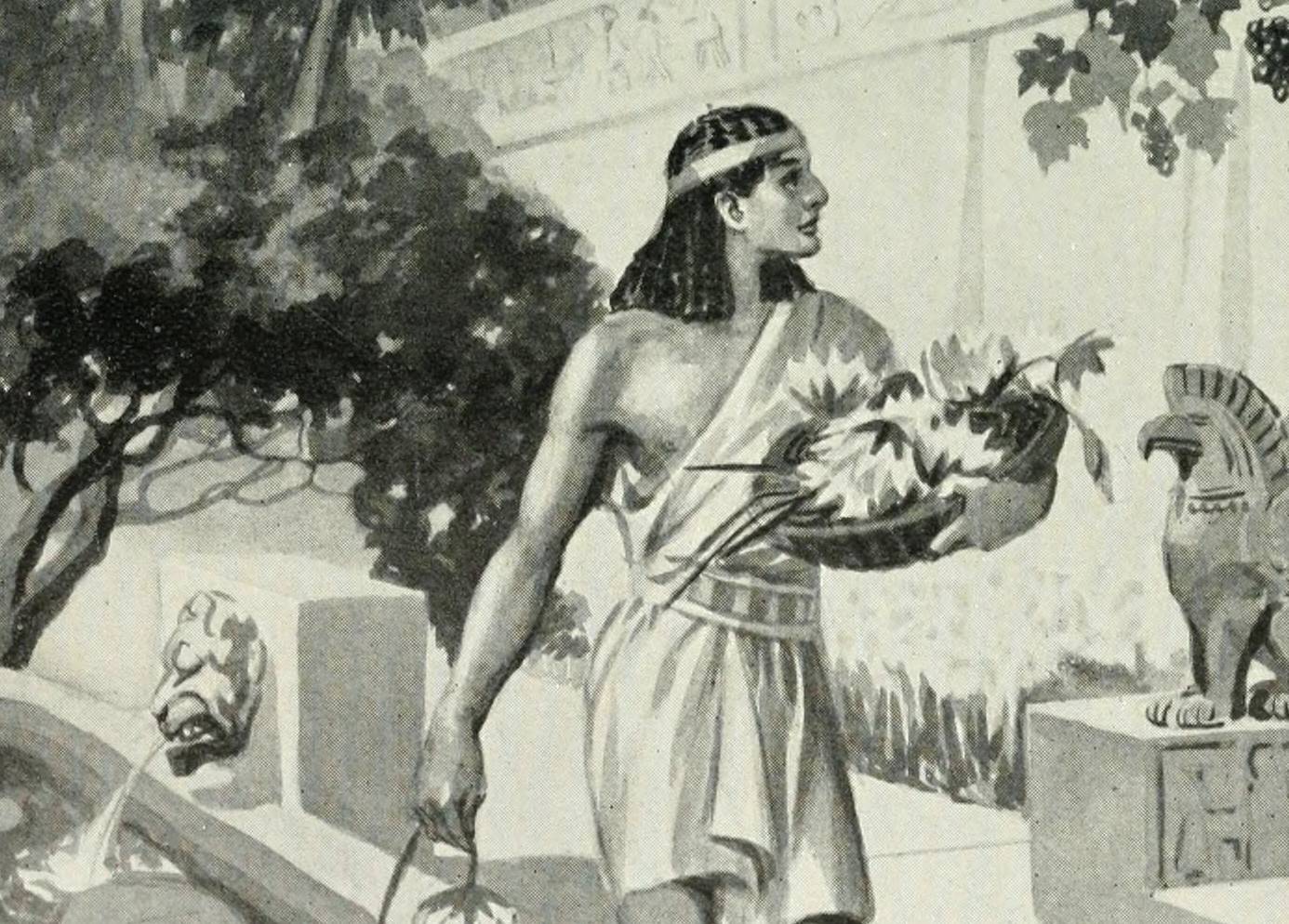
Sargon Of Akkad
Widely considered the first ruler of an empire in recorded history, Sargon of Akkad ruled the Akkadian Empire for 56 years from 2334 to 2279 BC. He ruled over an area that contained Mesopotamia (today made up of Iraq, Syria, Iran, Turkey, and Kuwait) and most of the Levant area (today made up of Jordan, Israel, Palestine, Lebanon, and Syria).
 Edwin John Prittie, Wikimedia Commons
Edwin John Prittie, Wikimedia Commons
Ashur-uballit I
Ashur-uballit I is considered the first king of the Assyrian Empire, which began when Ashur-uballit I began to expand his territory from the first city of Assyria, Assur, into other territories. This expansion soon covered an astonishing area of 540,000 square miles.
 A. C. Weatherstone (1888–1929), Wikimedia Commons
A. C. Weatherstone (1888–1929), Wikimedia Commons
Franz Joseph I
The Austro-Hungarian Empire, famous for you know what, began in 1867 when the Hungarian Parliament was re-established following a diplomatic resolution to intense conflict between the Ottoman-controlled areas of Austria. As such, Franz Joseph I became the King of Hungary, and new laws he created gave birth to the Austro-Hungarian Empire—which eventually invaded Serbia and other nearby states, until the Empire was dissolved on October 31, 1918, near the conclusion of the First World War.
 Edmund Tull, Wikimedia Commons
Edmund Tull, Wikimedia Commons
Sumuabum
The first known ruler of the Old Babylonian Empire was a man named Sumuabum. He began the Babylonian Empire by conquering the ancient cities of Dillbat and Kish (now modern-day Iraq), although one of his most significant achievements was beginning construction of a large wall around Babylon, which still stands today.
 Matson Collection, Wikimedia Commons
Matson Collection, Wikimedia Commons
Hammurabi
It would be remiss of us not to mention the rule of Hammurabi in this list. Although Sumuabum took control of a few small areas surrounding Babylon, it was Hammurabi who crafted the first major imperial gains for the Babylonians. His empire stretched 250 miles and he instituted the first known set of laws, referred to as the Hammurabi Code.
 Marie-Lan Nguyen, CC-BY 2.5, Wikimedia Commons
Marie-Lan Nguyen, CC-BY 2.5, Wikimedia Commons
Eweka I
Eweka I was the first King of Benin. Known as the Oba of Benin, he ruled from 1200 AD to 1235 AD, becoming the first Benin ruler to consolidate power under the monarchy, and left a legacy that rulers of the Benin people should be educated in the history and culture of Benin.
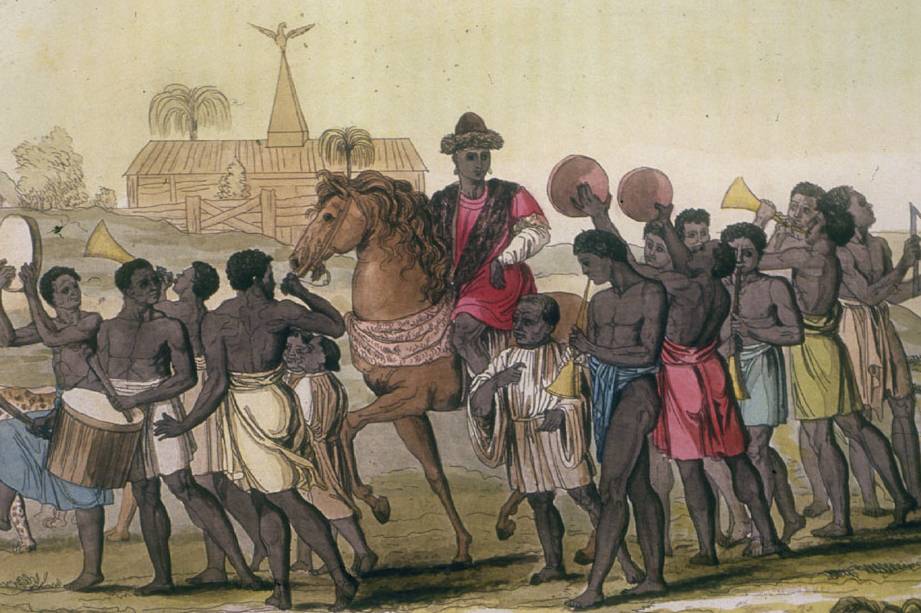 Giulio Ferrario, Wikimedia Commons
Giulio Ferrario, Wikimedia Commons
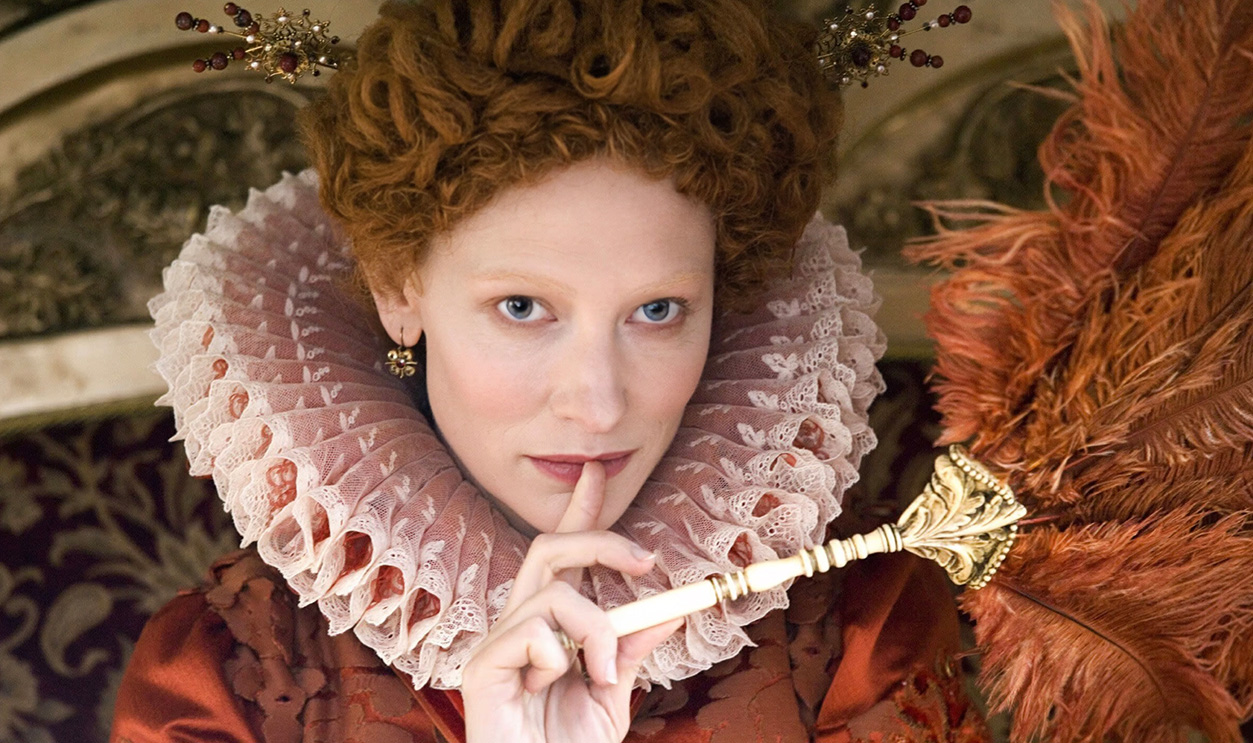
Elizabeth I
No list of empires would be complete without a mention of the British Empire. While the history of England stretches back 13,000 years, where there is evidence of continuous habitation, the British Empire did not begin until 1497, when John Cabot was sent out on a voyage to the Americas by Henry VII. Elizabeth I intensified this exploration of far-off lands, culminating in the establishment of an empire. Writer John Dee was the first person to use the term "British empire" when he was a political advisor to Elizabeth I in the mid-16th century.
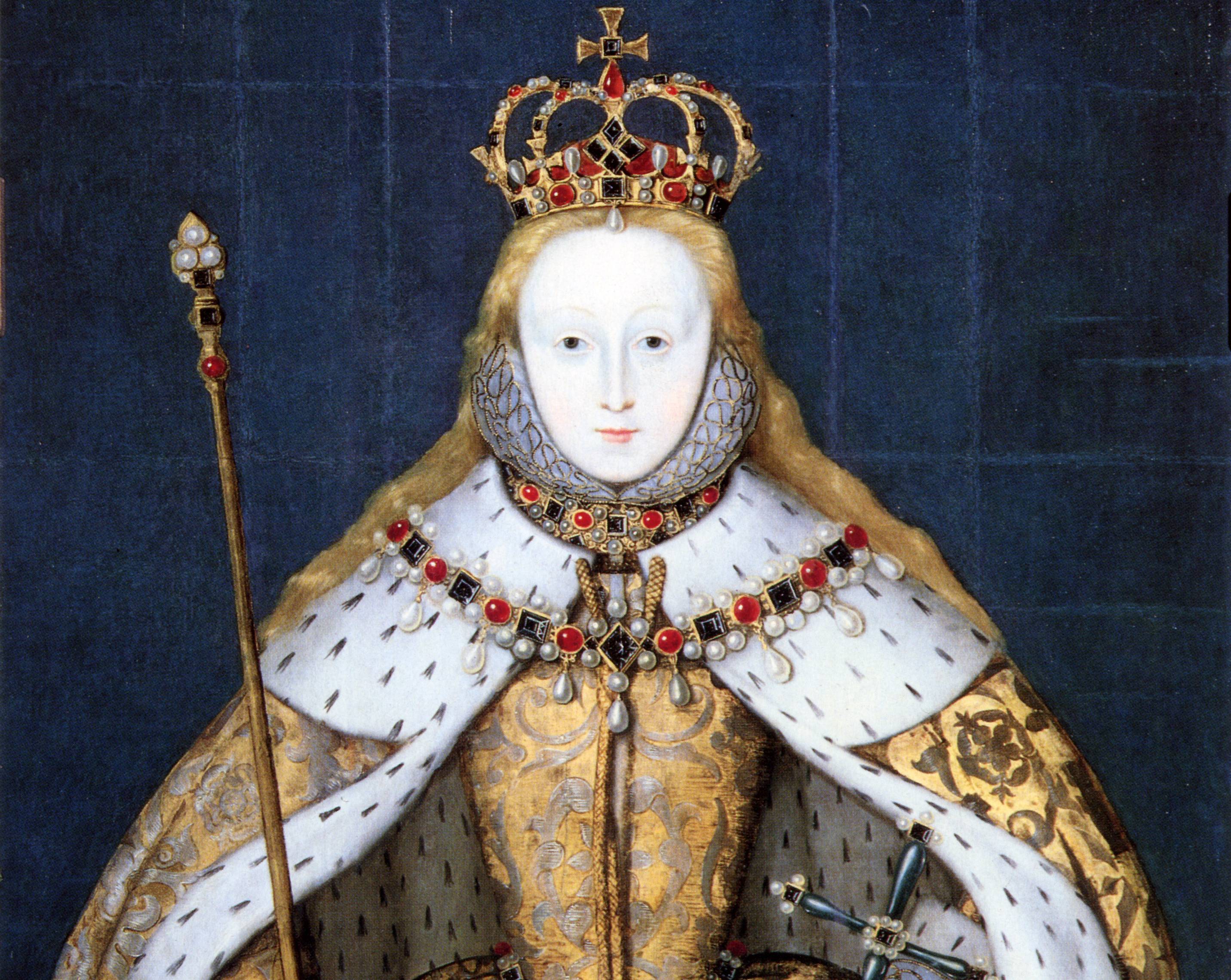 After Levina Teerlinc, Wikimedia Commons
After Levina Teerlinc, Wikimedia Commons
Sultan Muhammad Shah
Sultan Muhammad Shah established the first Kingdom of Brunei and ruled it as its first Sultan from 1368 till 1402. He would be the first in a long line of Sultans that would oversee Brunei until 1888, when Brunei became a British territory.
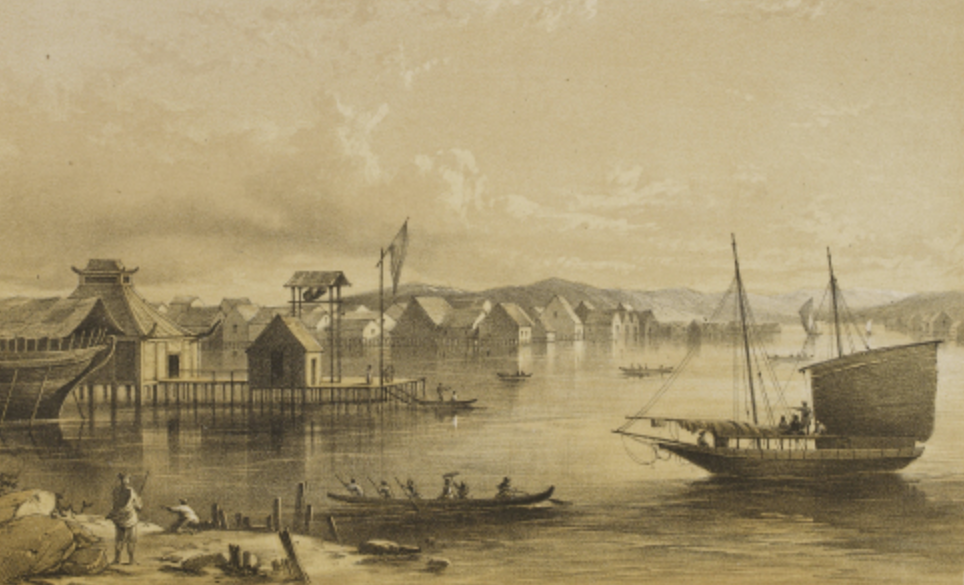 Frank S. Marryat, Wikimedia Commons
Frank S. Marryat, Wikimedia Commons
Pieter Both
Perhaps taking a page from the British book, the Dutch established a colonial empire that would last from 1602 until 1975, when the last bastion of Dutch rule in the East Indies, Suriname, declared independence. Beginning in 1602, the Dutch government began sending merchant sailing vessels to the East Indies and beyond, conquering territory and stealing resources. They set up a permanent seat of rule under the Dutch East India Company with the first governor-general appointment in 1610, when Pieter Both was appointed.
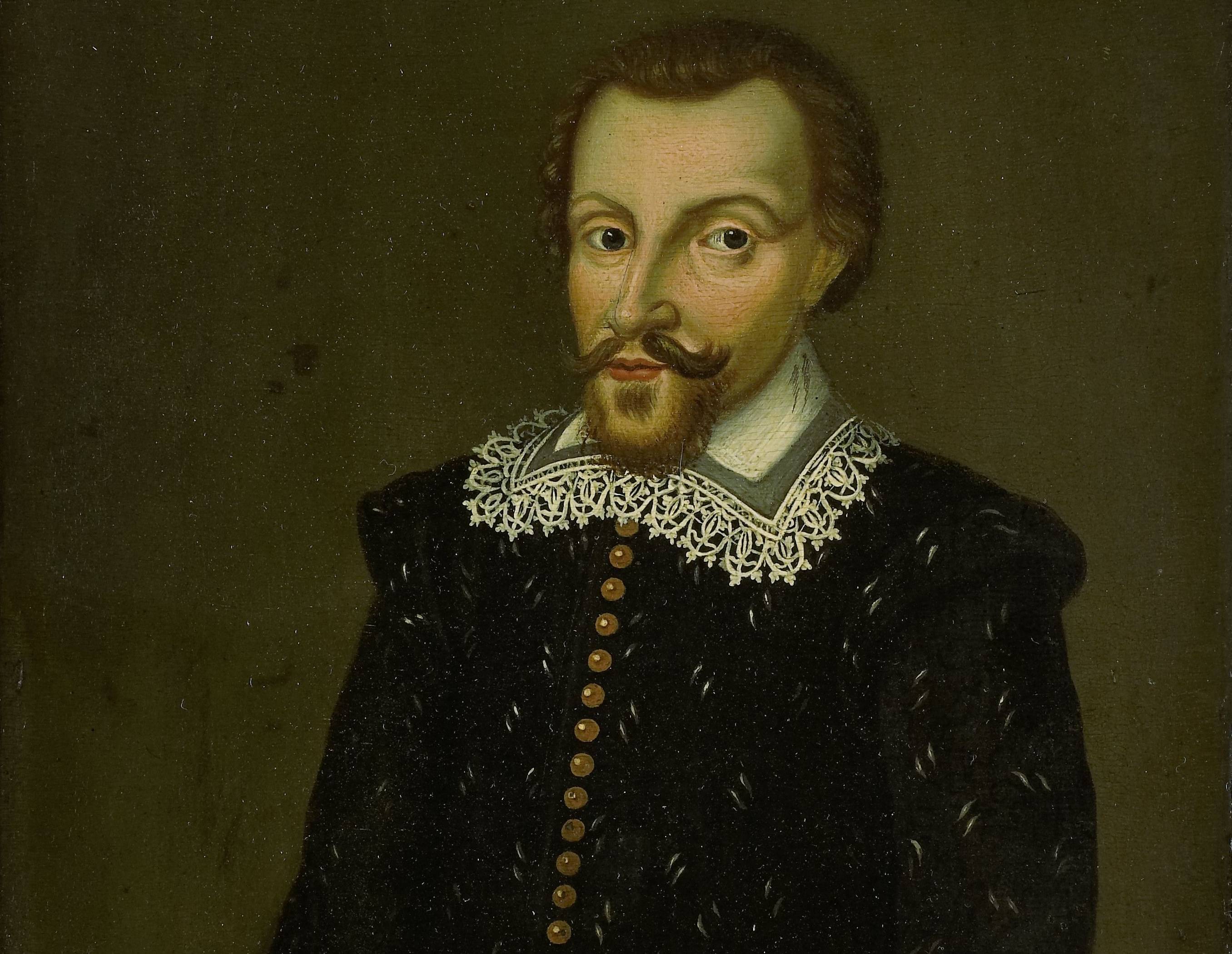 Rijksmuseum, Wikimedia Commons
Rijksmuseum, Wikimedia Commons
Otto Von Bismarck
Otto Von Bismarck was the Chancellor of the German colonial empire from 1884 until 1920. He oversaw the scramble for African resources from the major European powers, despite initially being resistant to colonizing other countries. He established the German colonial empire in 1884, but eventually ceded all North African territorial gains to the British in 1890.
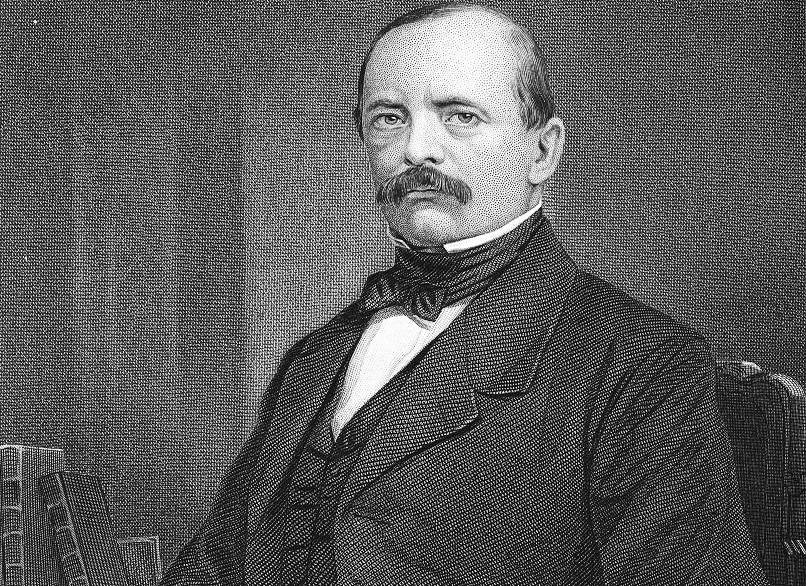 Evert Duykinck, Wikimedia Commons
Evert Duykinck, Wikimedia Commons
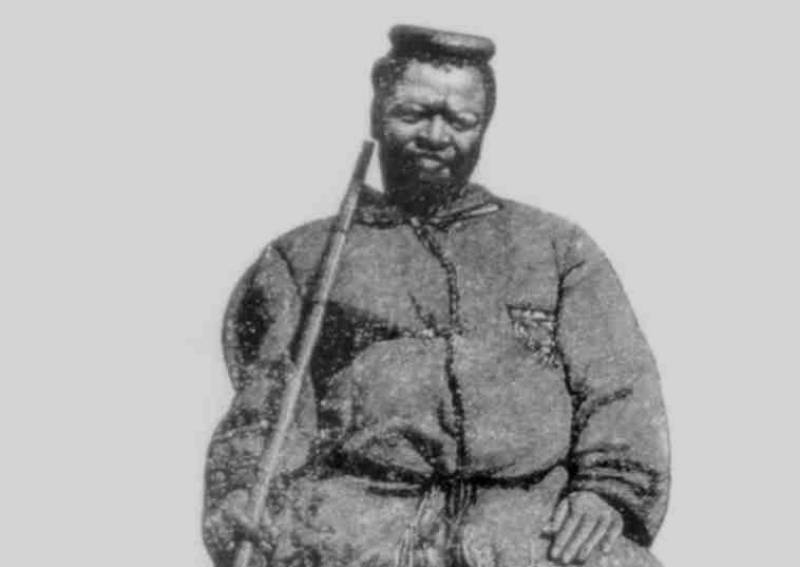
Shoshangana Zikode
Shoshangana Zikode was the founder and ruler of the Gaza Empire from 1825 till 1858, establishing a territory that represents most of modern-day Mozambique. Did you know that the province of Gaza in Mozambique was named after Shoshangana's grandfather, Gaza? And used to be called "Gazaland"?
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
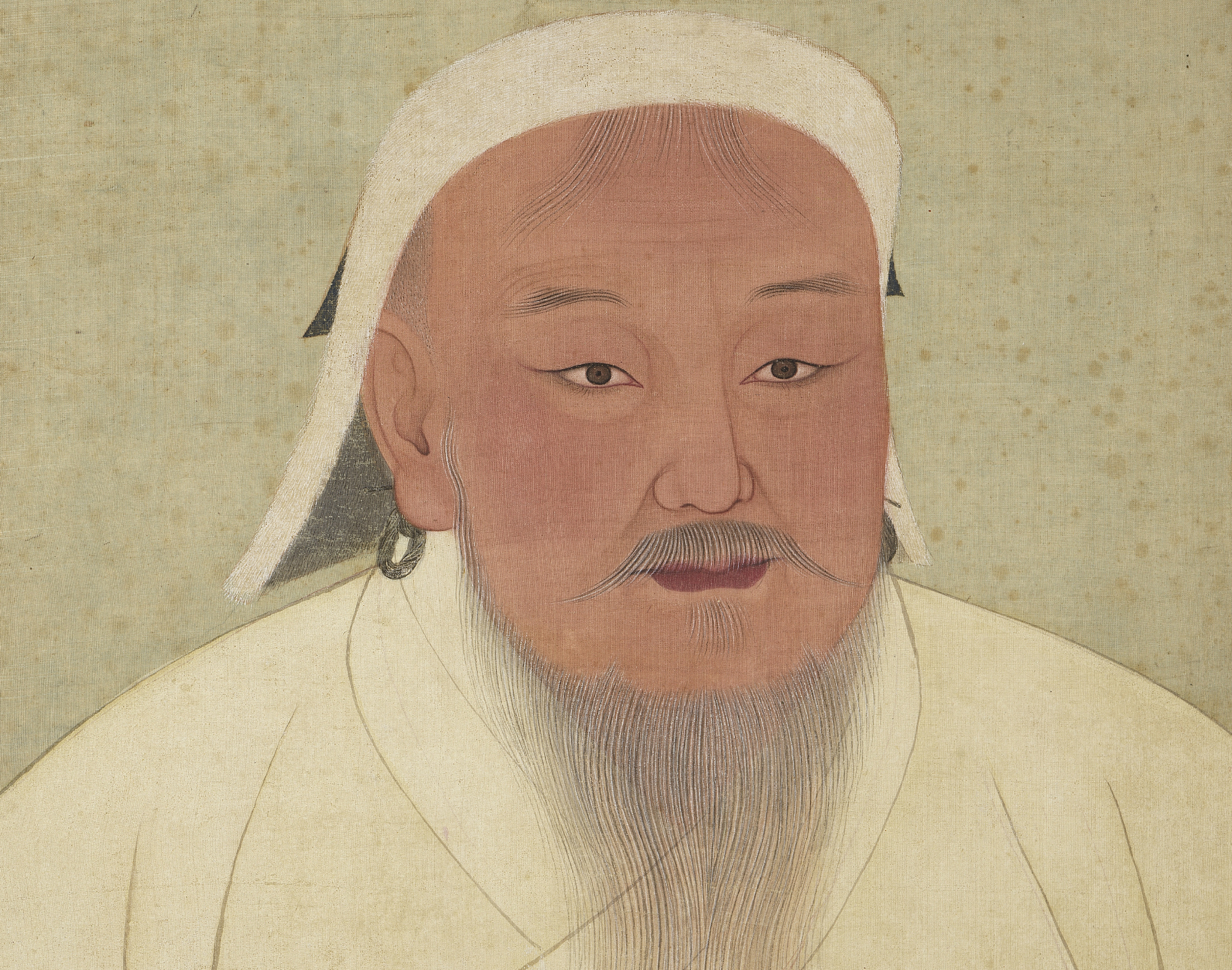
Genghis Khan
Of course, the first ruler of the Mongol Empire would have to be on this list. A formidable foe and mighty warrior, Genghis Khan saw the brutal and ruthless expansion of Mongolia as an empire, stretching from its westernmost point in modern-day Hungary to the China Sea in the east. That's an area of roughly 9 million square miles.
 National Palace Museum, Wikimedia Commons
National Palace Museum, Wikimedia Commons
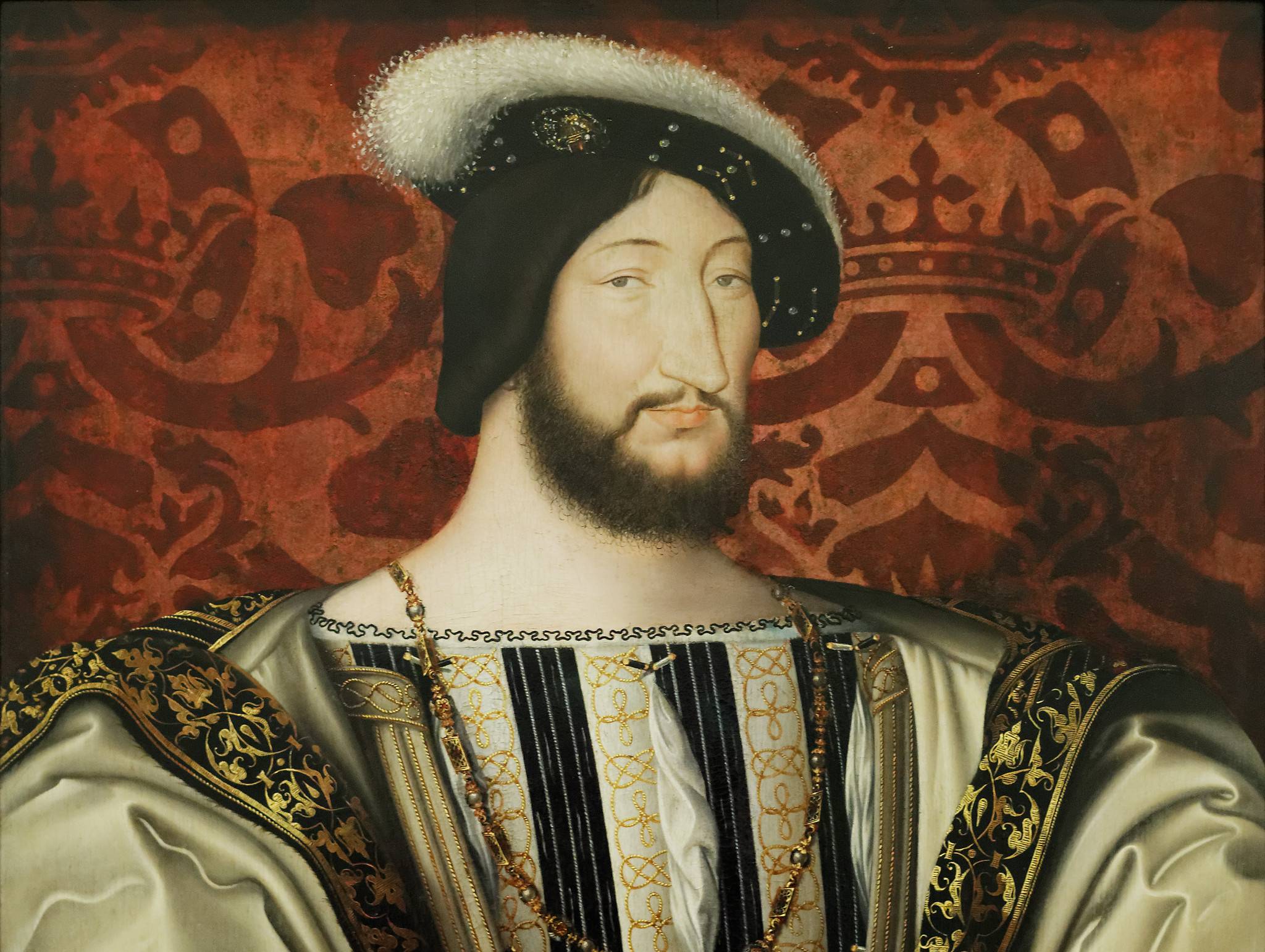
Francis I
The beginning of French colonial rule in North and South America began under the direction of Francis I, who dispatched French explorer Jacques Cartier to the shores of North America in 1605. However, a permanent French settlement in North America was not established until 1608, when Pierre Dugua and Samuel de Champlain established Port Royal in modern-day Nova Scotia, Canada.
 Jean Clouet, Wikimedia Commons
Jean Clouet, Wikimedia Commons
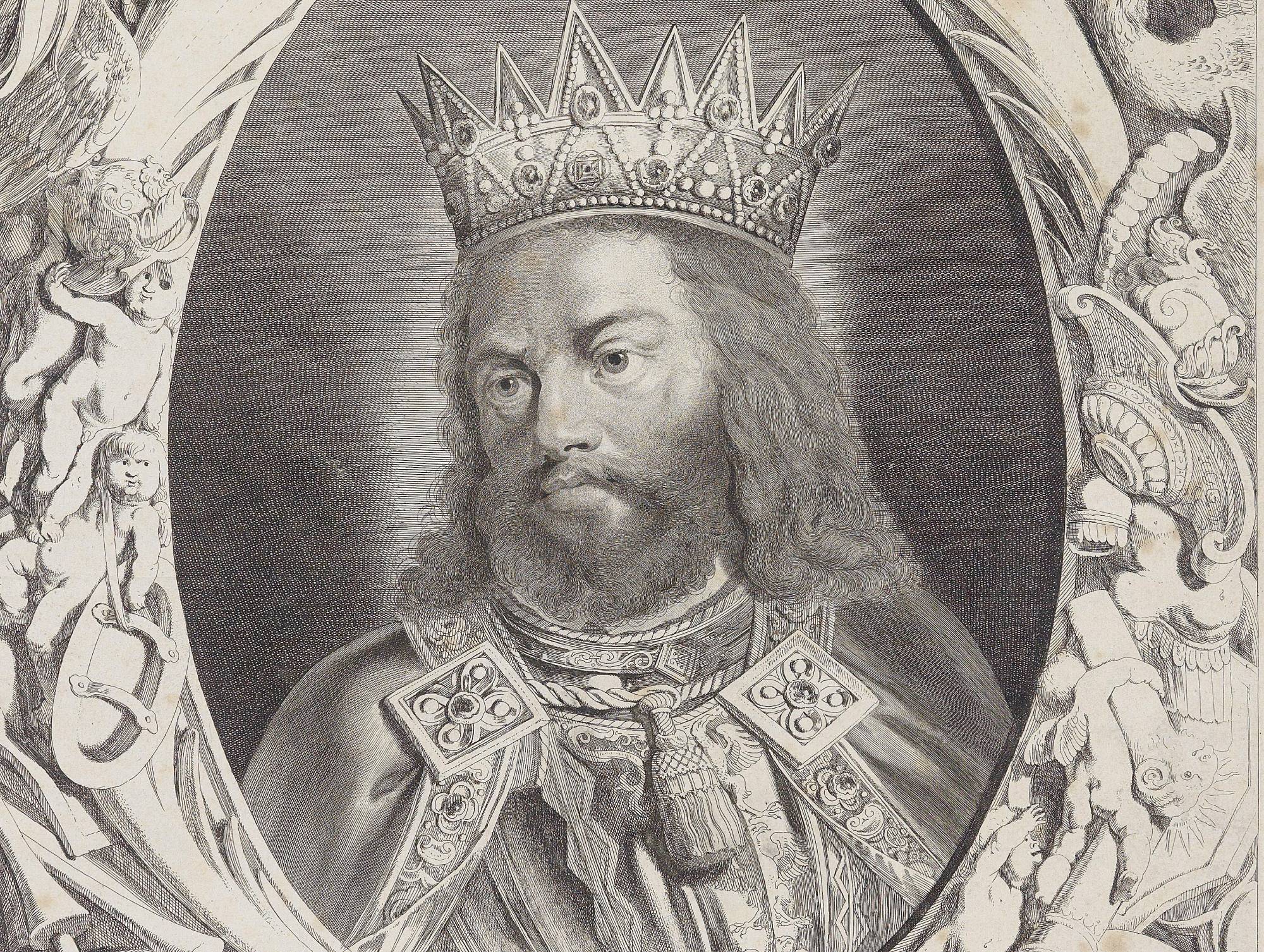
Rudolf I
Rudolf I was a German king who established the Habsburg Empire in 1279, after ruling over the Duchy of Austria, establishing the "Austrian Hereditary Lands". But it wasn't until 1482, when Maximilian I married a Dutch woman and brought parts of the Netherlands into Habsburg control, that the Empire extended its reach significantly beyond Austria.
 After Pieter Soutman, Wikimedia Commons
After Pieter Soutman, Wikimedia Commons
St Stephen I
The first ruler of the Kingdom of Hungary was St Stephen I, established as a Christian king following his coronation on Christmas Day in the year 1000 AD. Territorial expansions under Stephen I were limited, but his successors ushered in the first Hungarian Empire by taking control of modern-day Slovakia and Croatia, establishing an empire that ruled until 1301 AD.
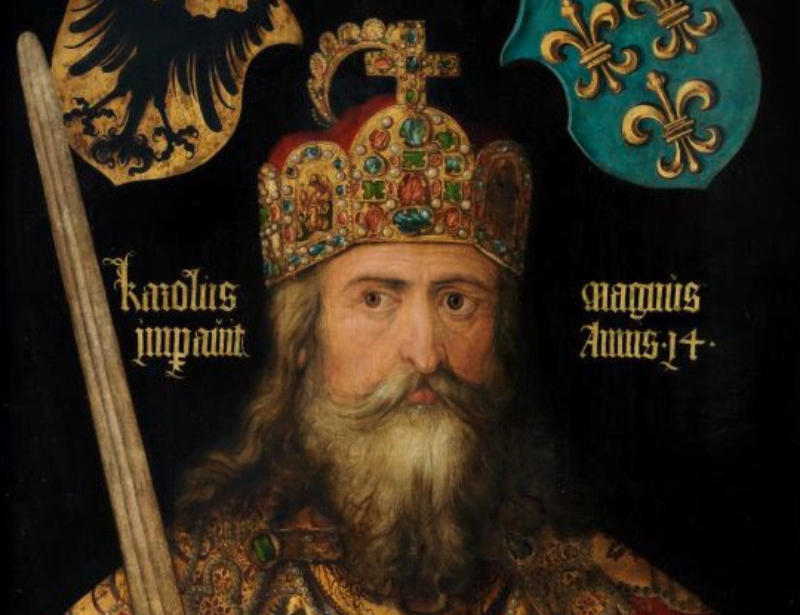
Charlemagne
Charlemagne is widely thought to be the first ruler of the Holy Roman Empire, after being crowned by Pope Leo III in 800 AD. Charlemagne would begin an empire characterized by political, military, and religious supremacy that would last almost a thousand years, until the Holy Roman Empire was disbanded in 1806.
 Albrecht Dürer, Wikimedia Commons
Albrecht Dürer, Wikimedia Commons
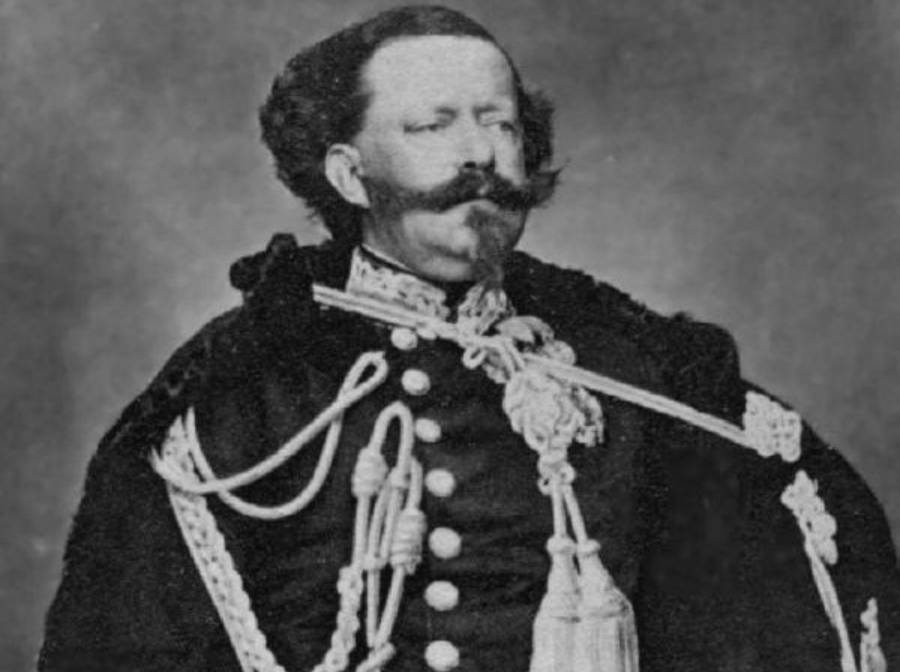
Victor Emmanuel II
Victor Emmanuel II was the first King of a restored Italian Empire, following the defeat of Napoléon Bonaparte and the unification of more territory under Italian rule from 1848 until 1870. Italy had been a divided country since the 6th century, mostly controlled by various religious-political figures. Victor Emmanuel II fought in the first Italian War of Independence and gained the Kingdom of Sardinia. His reign would last until 1878, but the Italians would be an imperial power until 1943.
 André-Adolphe-Eugène Disdéri, Wikimedia Commons
André-Adolphe-Eugène Disdéri, Wikimedia Commons
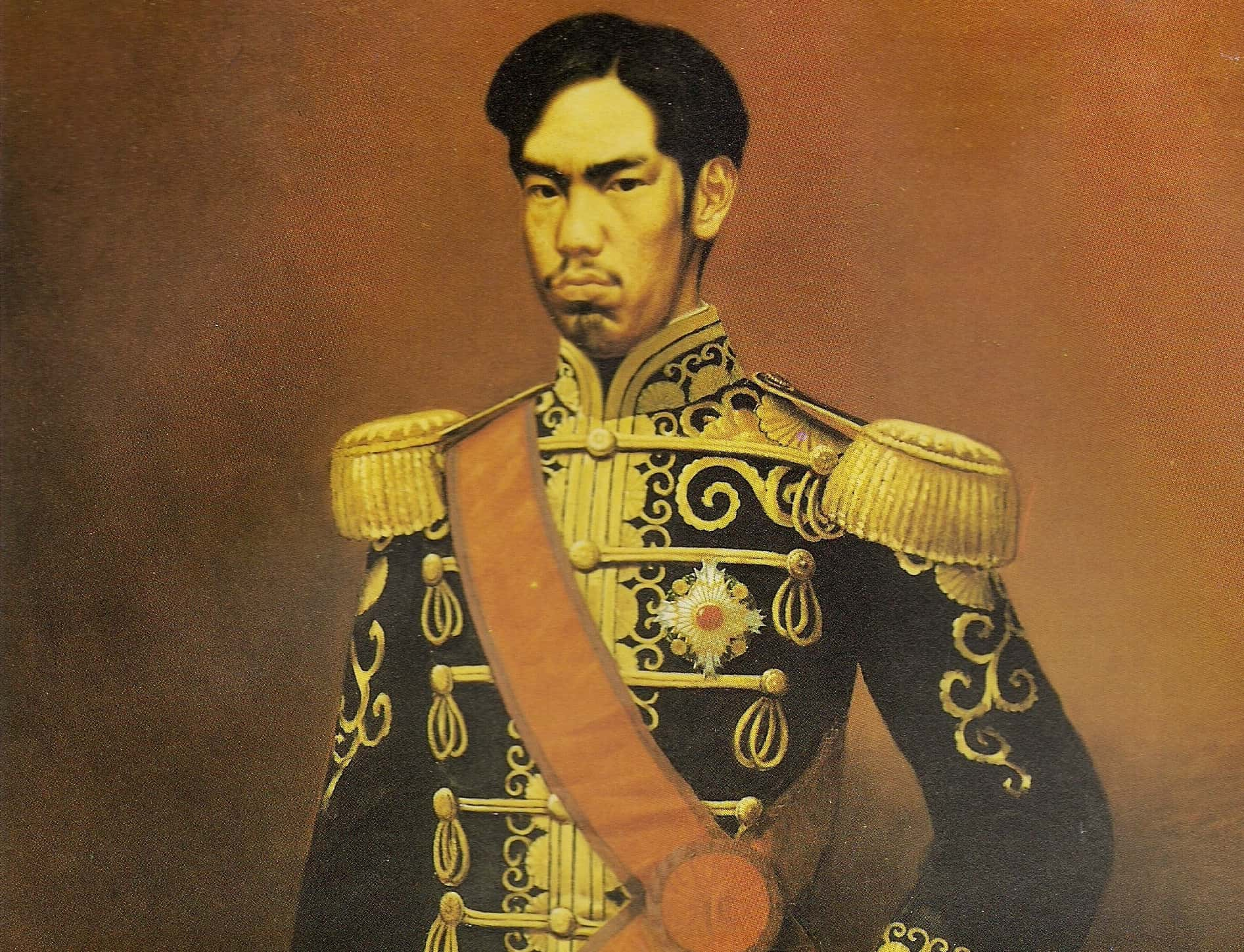
Emperor Meiji
Mutsuhito, otherwise known as Emperor Meiji, was the first emperor of Japan during the Imperial Japanese era from 1848, following the dissolution of the Boshin Shogunate which had ruled over a feudal Japan for 200 years. Meiji's reign lasted until 1912 and oversaw the Boxer Rebellion, the Russo-Japanese War and the Annexation of Korea.
 Takahashi Yuichi (1828-1894), Wikimedia Commons
Takahashi Yuichi (1828-1894), Wikimedia Commons
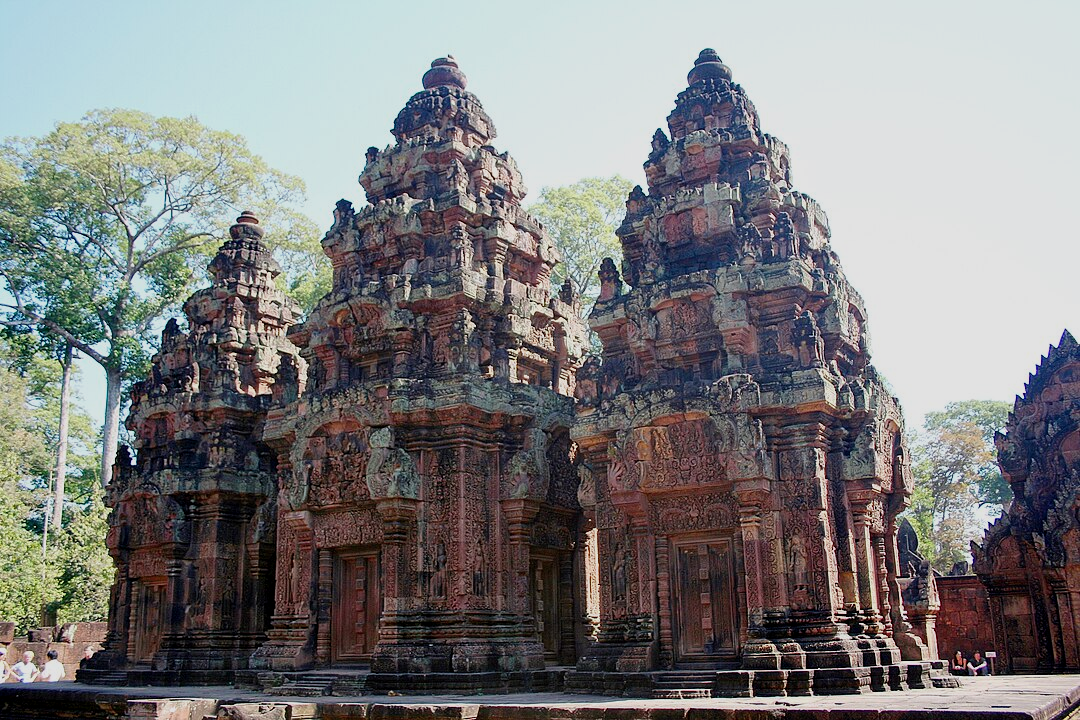
Jayavaraman II
The reign of Jayavaraman II of the Khmer Empire was a pivotal point in shaping Southeast Asia today. He established the Khmer Empire, defying the Cambodian monarchy in 802 CE, and built a territory through military conquest that was 390,000 square miles at its peak.
 083794703875938, Wikimedia Commons
083794703875938, Wikimedia Commons
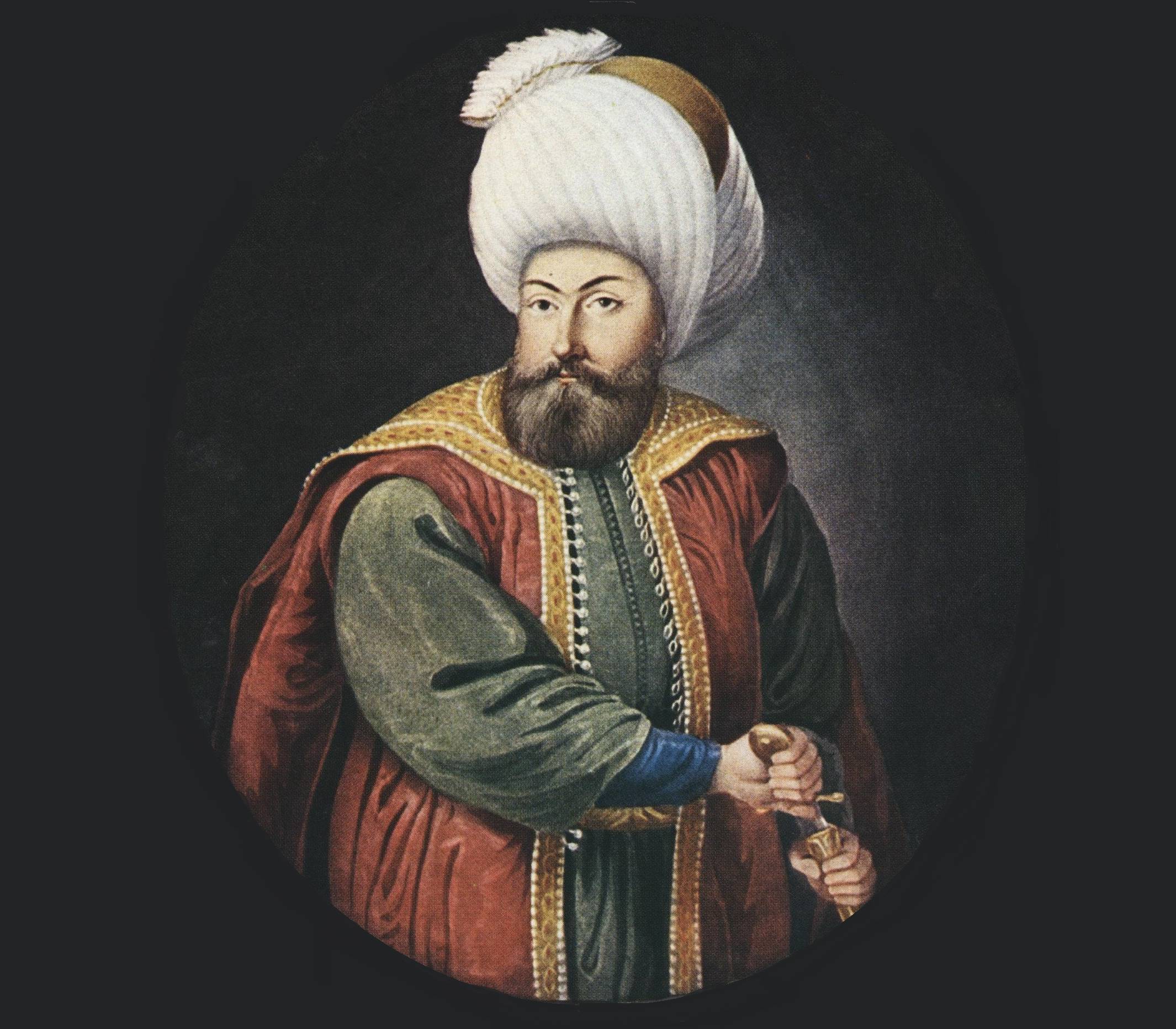
Osman I
Osman I is widely considered to be the first ruler of the Ottoman Empire, beginning his reign in 1302, after defeating the Byzantine Army at the Battle of Bapheus. He would establish a vast empire that was expanded upon after his death in 1323. Known as "beyliks", or areas under the administration of the Ottomans, his lands would culminate in 19.9 million square miles of territory at their peak.
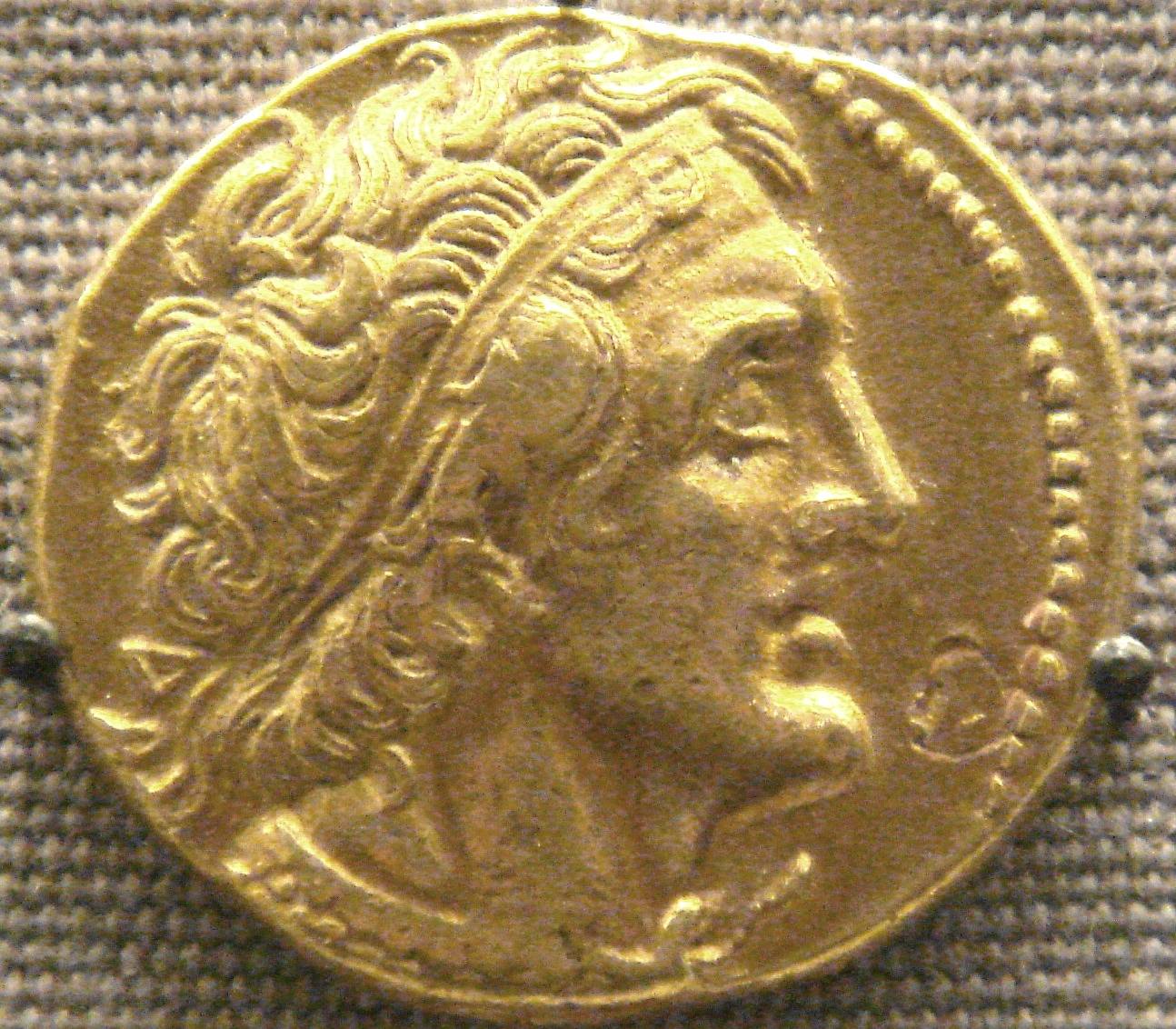
Ptolemy I
Ptolemy was a Macedonian general who oversaw the Ptolemaic Empire—as a trusted friend of Alexander The Great, he inherited much of his 2 million square mile empire, ruling from 302 to 285BC.
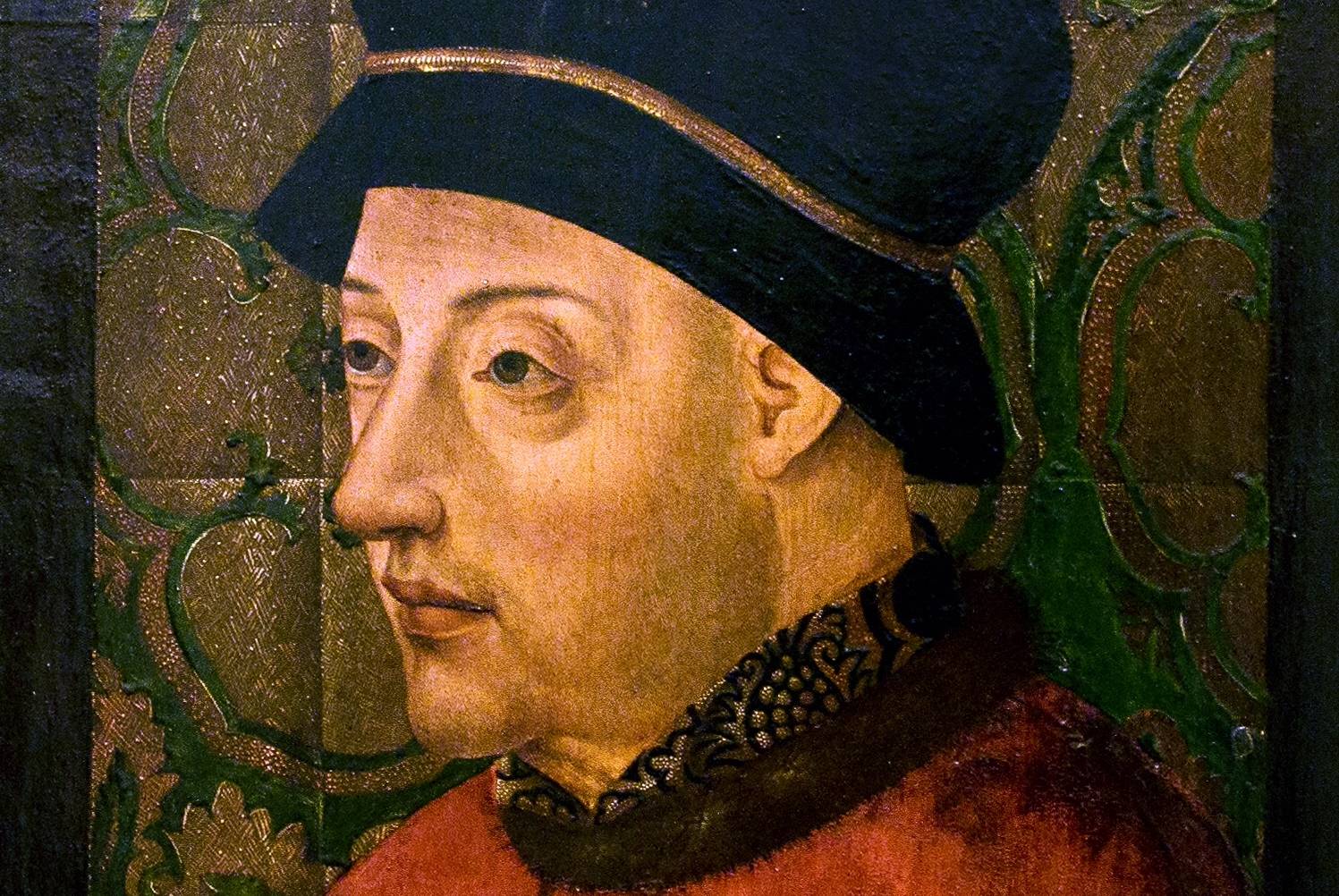
John I
John I was the first King of Portugal who oversaw the beginning of the Portuguese Empire, by taking over the Atlantic islands of Madeira and Azores in 1419 and 1427, spending the rest of the 15th century expanding Portuguese authority into Africa. His death after 48 years on the throne saw Portugal become one of the major maritime powers in Europe.
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
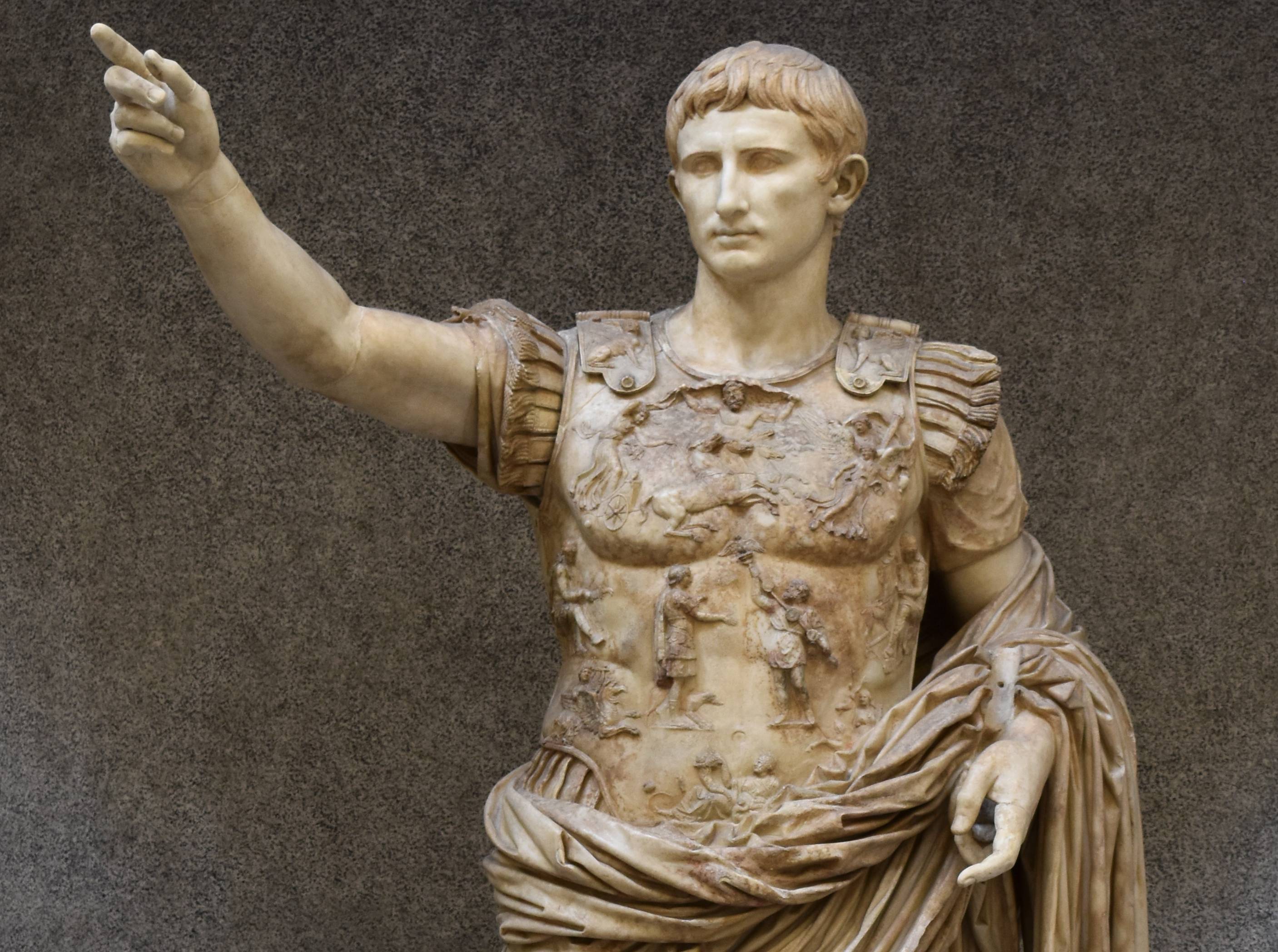
Augustus
Following the assassination of Julius Caesar in 44 BCE, Augustus laid claim to Rome and restored it as a Republic in 27 BCE, despite retaining all the power for himself as the "first citizen". Augustus began conquering territory during the final years of his reign, leading up to an empire that would span 9 million square miles at its peak.
 Vatican Museums, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Vatican Museums, CC BY-SA 4.0, Wikimedia Commons
Ivan The Great
Despite Peter I being the first Emperor of Russia, Ivan The Great laid the groundwork for him—so we'll give the devil his due here. Ivan The Great successfully unified hundreds of small princedoms under the administration of Moscow, including an area throughout Siberia, and stretching from modern-day northern Finland to Poland in the West.
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
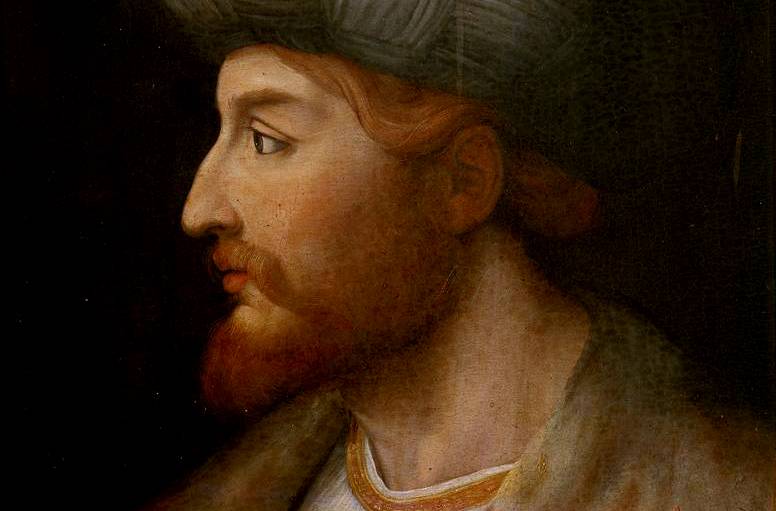
Shah Ismail I
Shah Ismail I was the first ruler of the Iranian Safavid dynasty. The self-declared Shah unified the Iranian localities under the Safavid dynasty and began a war with the Ottomans. The Shah ruled Iran and much of the southern part of the Middle East and southeastern Europe. He also established Shi'a Islam as the official state religion.
 Uffizi Gallery, Wikimedia Commons
Uffizi Gallery, Wikimedia Commons
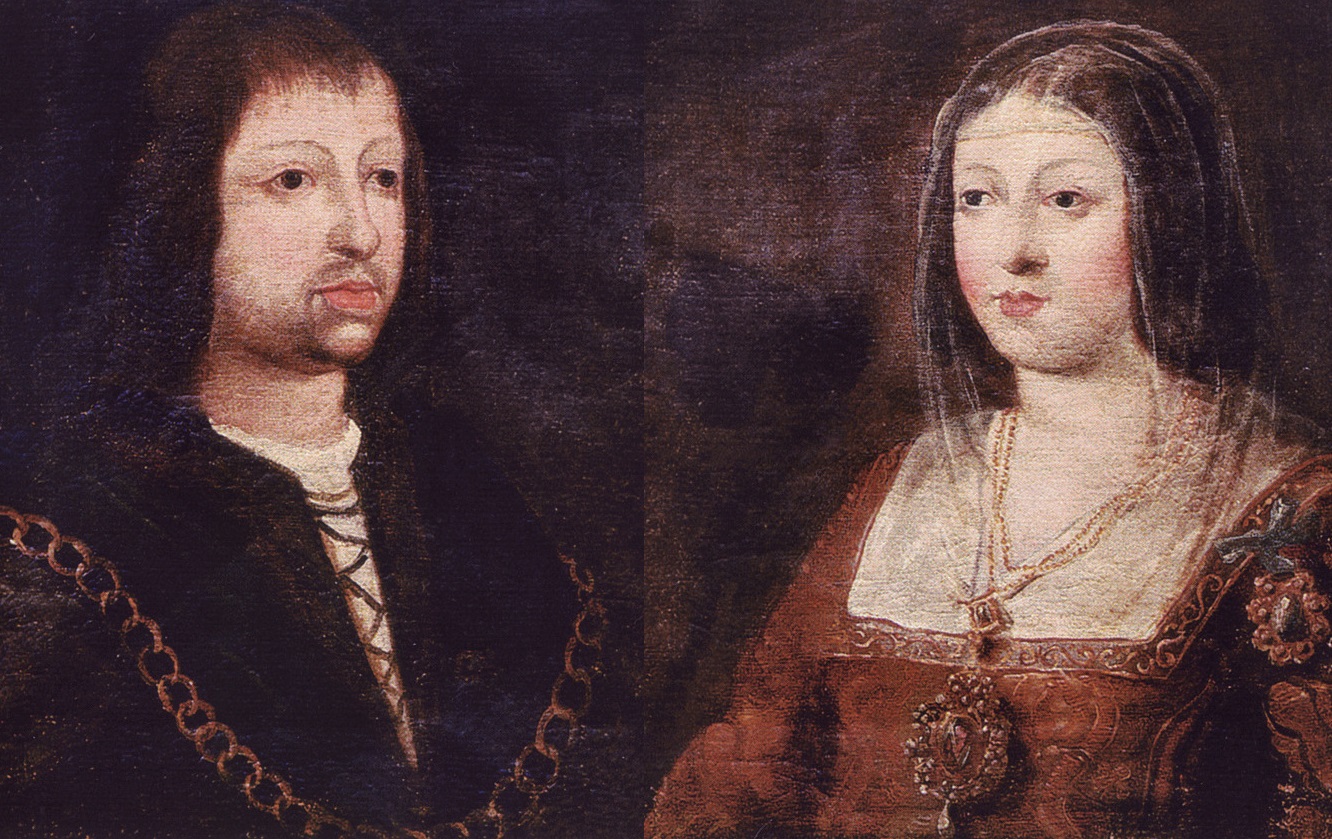
Ferdinand Of Aragon & Isabella Of Castile
Ferdinand of Aragon and Isabella of Castile are widely viewed as the pair that established the Spanish monarchy and would also be the pairing that set Spain on the path to Inquisition, thanks to the heavy influence of the Catholic Church. The Spanish Empire took over most of the Americas, the Caribbean, and backed the first circumnavigation of the Earth by Magellan in the early 16th century. At its peak, the empire ruled 5 million square miles of territory around the world.
 Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
Unknown Author, Wikimedia Commons
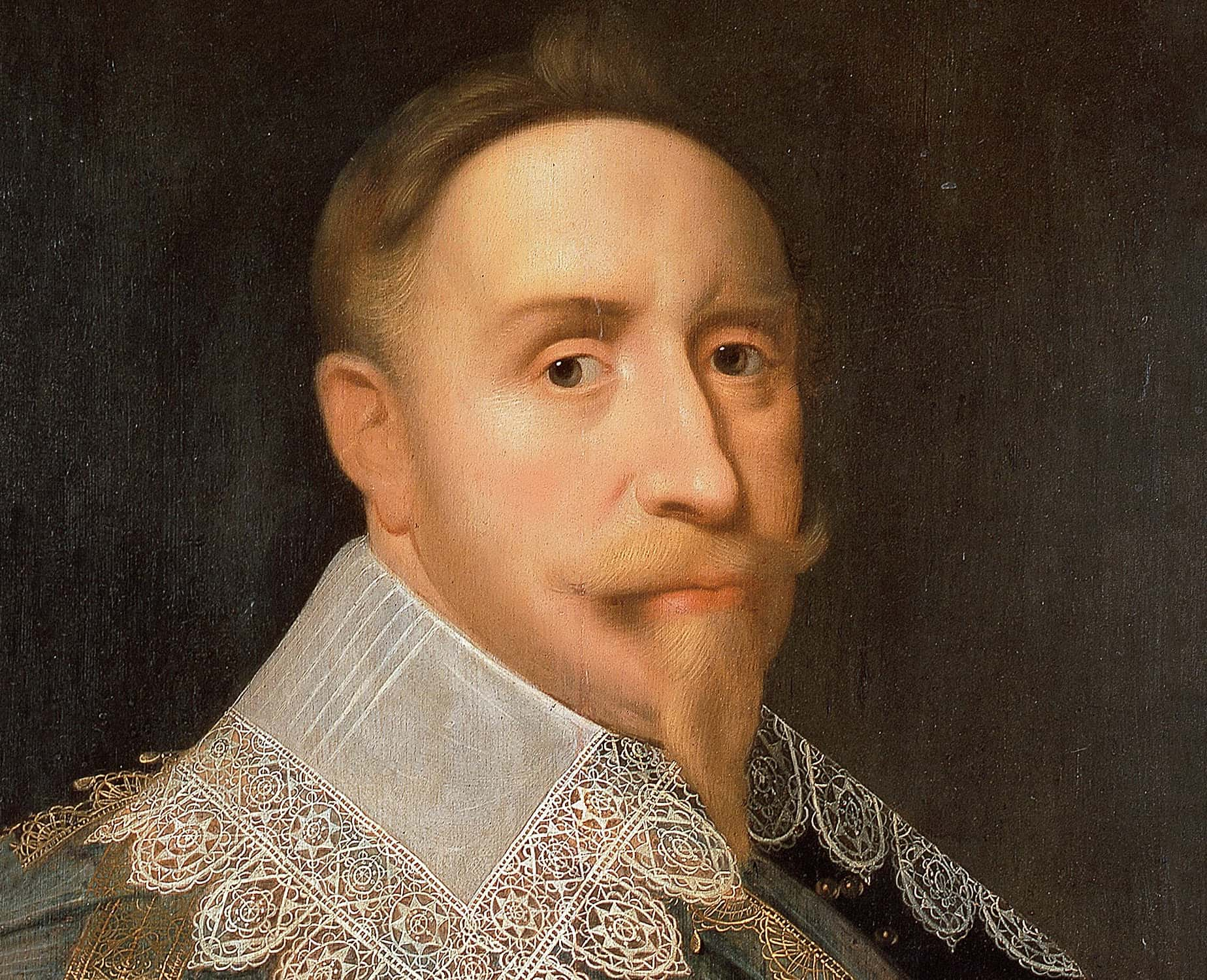
Gustavus Adolphus
The Swedes aren't the first people that would come to mind when thinking of great imperial powers—but Gustavus Adolphus changed all that in 1611 when he ascended the throne. He began a policy of "soft power" through diplomacy and "hard power" through military conquest that saw Sweden expand its control to take over much of Finland and other Baltic states through regency authorities, particularly after his death in 1632. It covered an area of 185,000 square miles.
 Jacob Hoefnagel, Wikimedia Commons
Jacob Hoefnagel, Wikimedia Commons
Baldwin I
Baldwin I was the ruler of the Latin Empire, beginning in 1204 with the Fourth Crusade. His original goal had been to recapture the holy city of Jerusalem from Salahuddin, a Muslim leader who had taken the city. But Baldwin's attention was instead drawn to Constantinople, the capital city of the Byzantine Empire. Capturing the city in April of 1204, Baldwin I began the Latin Empire, which would span 80,000 square miles at its peak.
 Merry-Joseph Blondel, Wikimedia Commons
Merry-Joseph Blondel, Wikimedia Commons
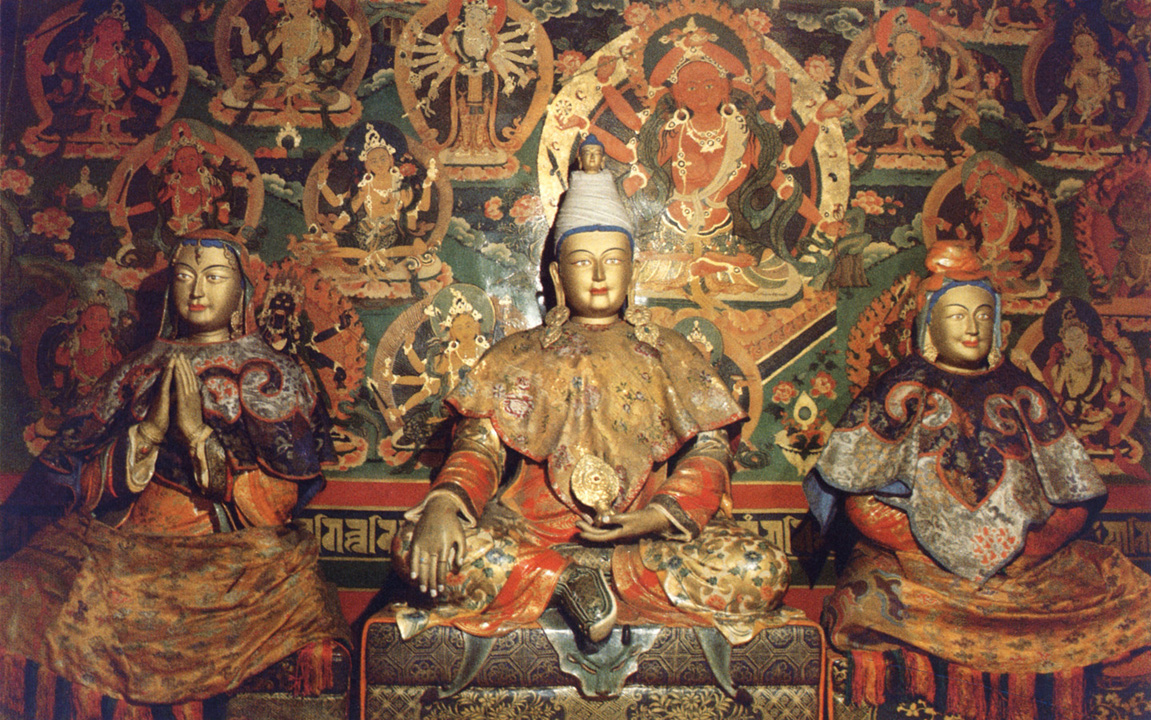
Songsten Gampo
You might not think of Tibet as a place of imperial power in the East, but it was during the 7th century, when Songsten Gampo became the 33rd Tibetan King and the ruler of the Yarlung Dynasty. Along with formally introducing Buddhism to Tibet, he also conquered adjacent territory, including modern-day Afghanistan and parts of northern India.
 Ernst Stavro Blofeld, Wikimedia Commons
Ernst Stavro Blofeld, Wikimedia Commons
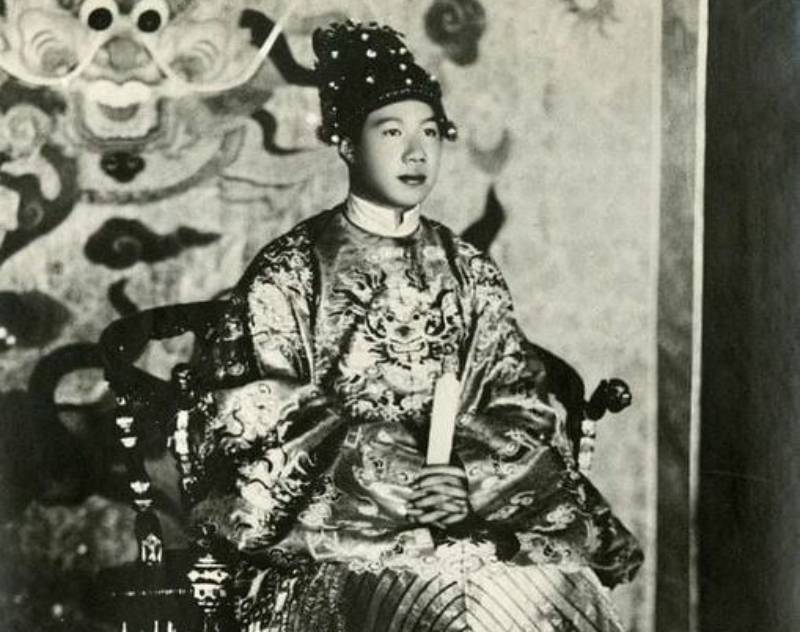
The Second-Shortest Empire In History
Not quite the shortest empire in history—but almost—the Empire of Vietnam began when Emperor Bào Ðài created the empire, after declaring independence from France on March 11, 1945. Little more than a puppet state of Imperial Japan, the Vietnamese Empire did not last long—it was dissolved on August 14, 1945 when the Viet Minh seized control of the country.










