The world of science is forever evolving, with discoveries constantly pushing our society forward into a brighter and better future every day. Researchers today can conduct complex studies and arrive at groundbreaking conclusions thanks to the trailblazing work of dedicated scientists from a time past. Perhaps one of the most influential scientists in history is Marie Curie, the Mother of Radiology. Her contributions to science are some of the most crucial, and she achieved them all despite facing several obstacles. This is her story, both inspirational and awe-inspiring.
A true academic from the start
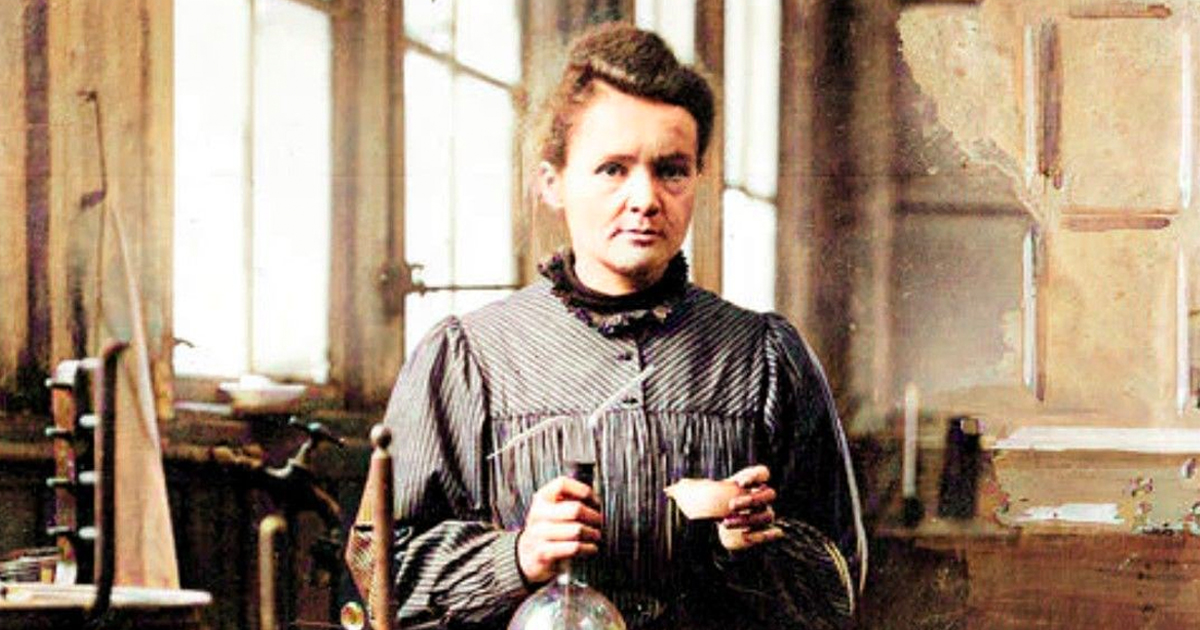
Born in Warsaw, Poland on November 7, 1867, as Maria Skłodowska, Marie Curie overcame many challenges to become one of history's greatest scientists ever. Her life served as a shining example of academic brilliance, resolute perseverance, and an unwavering dedication to the advancement of science. Curie's pioneering work in the area of radioactivity earned her not one, but two Nobel Prizes, as well as a lasting legacy that continues to inspire generations of scientists after her.
Curie showed an intense passion for learning from a young age, even despite her family's financial struggles. It was extremely difficult for a woman to pursue higher education in the late 19th century as most institutions were male-dominated and not so open to having female members. She did, however, relocate to Paris in 1891 to pursue degrees in mathematics and physics at the Sorbonne. Curie struggled with poverty and frequently took on odd jobs to pay for her education. Her commitment to academia soon gained the attention of her teachers, who saw her untapped potential.
A glowing partnership, in love and career
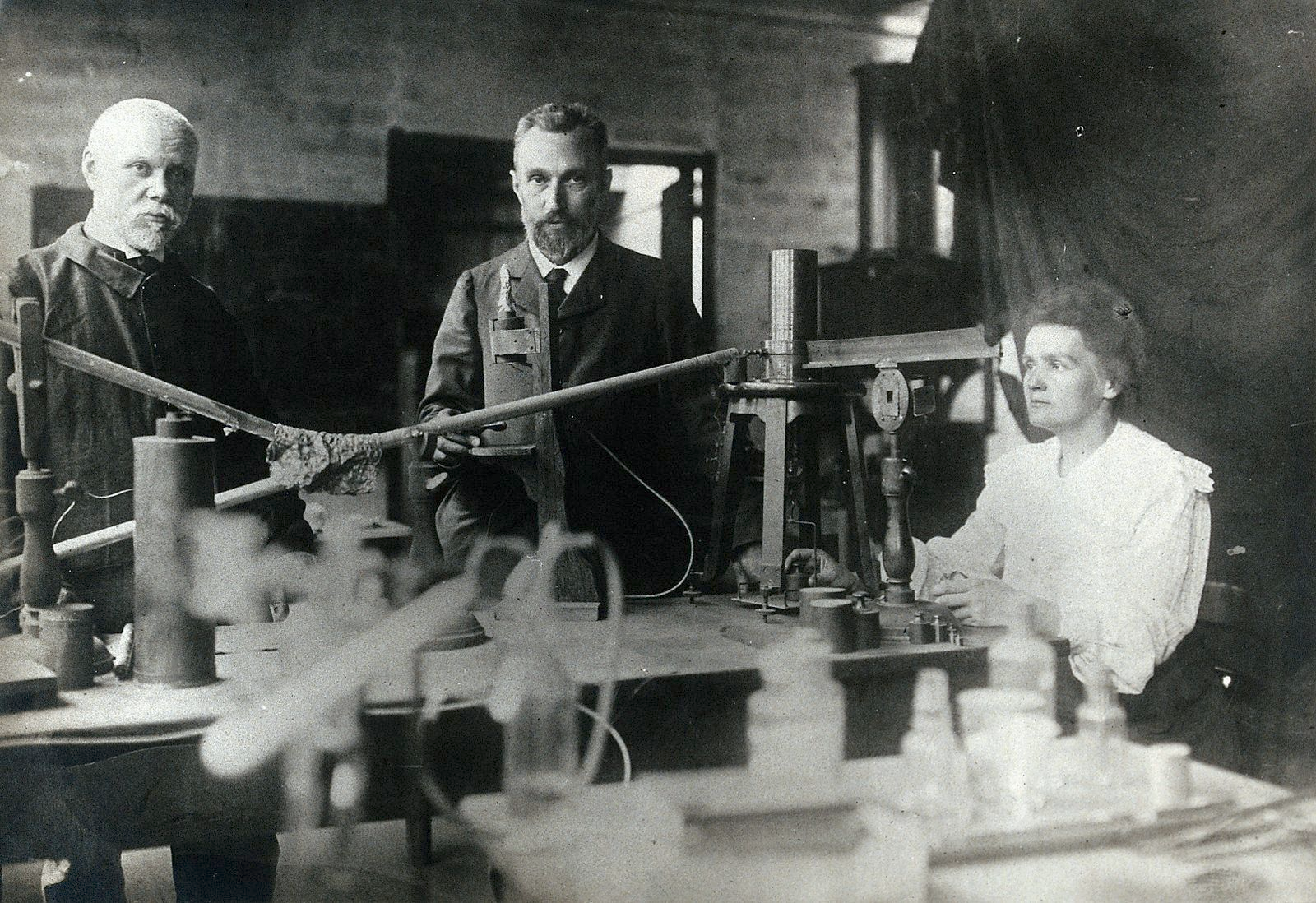
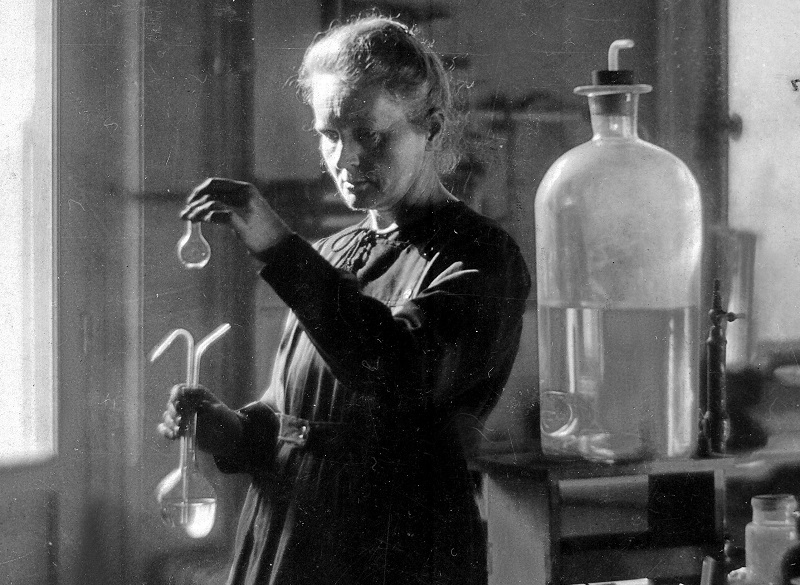
Later in her career, she would meet (and eventually marry) her colleague Pierre Curie. Their scientific collaboration would not only change her life but alter the course of history. In 1895, they explored the brand-new field of radioactivity—a term that Marie herself had coined. Their combined research resulted in the identification of two new elements, radium and polonium, as well as the novel concept that some elements were innately radioactive.
Marie became the first woman to win a Nobel Prize in Physics in 1903, thanks to her and Pierre's breakthrough research. However, the achievement was overshadowed by a general mistrust of her work, which was fueled by discrimination as a result of her gender. Unfazed, she conducted more research and, in 1911, she was awarded a second Nobel Prize in Chemistry for her work isolating polonium and radium and studying their characteristics.
Though Marie Curie is most known for her revolutionary studies, she also put forth other game-changing contributions that shaped history. Among them was the creation of portable radiography devices, dubbed "Little Curies," to give X-rays for medical imaging on the front lines during the World War I effort. It further demonstrated just how important her work was, as it applied to non-science fields as well.
The downhill spiral
Despite her remarkable success, Curie faced many personal tragedies. In 1906, Pierre Curie lost his life in a tragic car accident, leaving Marie widowed and a single mother of two small daughters. She accepted her husband's chair at the Sorbonne, becoming the first woman to teach at the university, despite her sadness. Her strength in the face of difficulty was seen by her will to carry on their scientific legacy.
Even more tragic, Curie would be diagnosed with aplastic pernicious anemia at 66 years old, a condition she developed over the years due to exposure to radiation through her work. The fact that her rise and fall both came from the study of radioactivity led to many people to call her the "Mother of Radiology." a fitting title for a remarkable woman.
All in all, Curie's contributions set the stage for major developments in nuclear physics, medicine, and many other areas. Marie Curie made a lasting impact on science while also breaking social norms, proving that success is genderless. Aspiring scientists could find inspiration from her story to overcome their own challenges and pursue knowledge with the same courage.