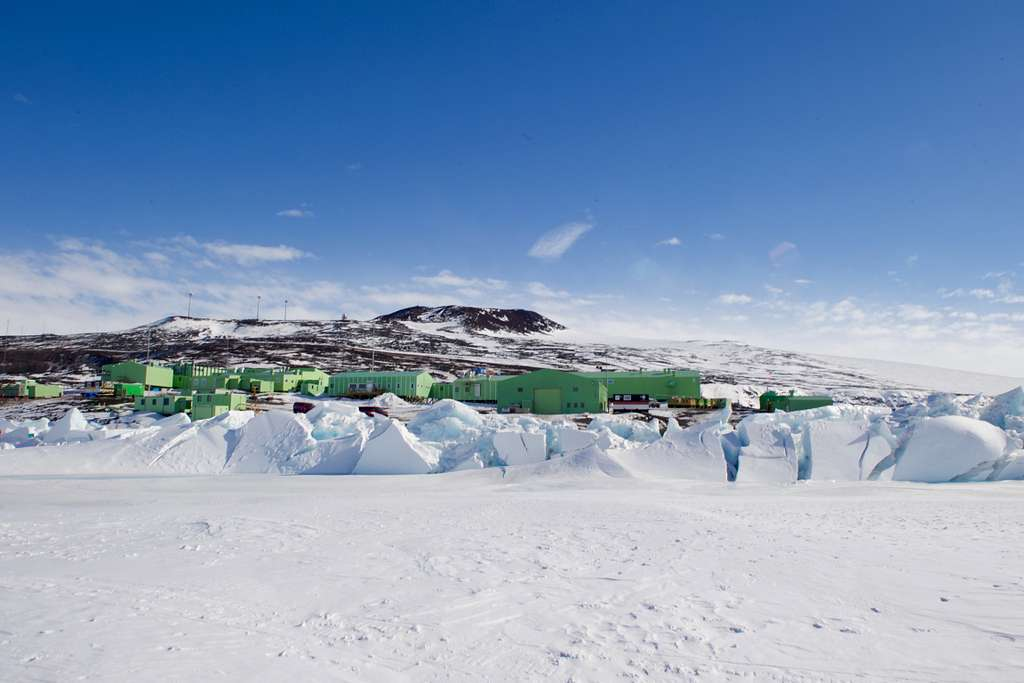
Under the frozen surface of Antarctica, scientists have discovered a buried ancient landscape that has captured the attention of both the scientific community and the general public. This discovery is considered significant—the frozen area, which has been preserved for millions of years, provides a rare glimpse into the distant past of Earth and may reveal new insights about the planet's geological and climatic past.
Modern technology, like as satellite photography and ice-penetrating radar devices, allowed for this discovery. Underneath its vast ice sheets, Antarctica is believed to conceal a rich geological history that has long been speculated by scientists. Recent discoveries have revealed a region that has been unexplored for ages.
Signs of ancient plant and animal life
The ancient landscape is said to have originated back when Antarctica was a bustling, temperate location filled with life, rather than the desolate icy continent it is today. Fossil evidence contradicts the idea that Antarctica has always been a barren cold wasteland by indicating that the continent was formerly home to lush forests, a wide diversity of ancient animal species, and diversified vegetation.
The discovery of well-preserved fossilized remnants, including plant and animal species, is one of the most remarkable finds. The fossils offer a look into an earlier era, enabling researchers to piece together the development of Antarctica over many geological periods. This discovery might provide insight into the planetary processes that gave rise to the Antarctic climate that exists today, providing answers to decade-long questions on the dynamics of Earth's past climate and the development of its ecosystems.
 NASA Goddard Space Flight Center | Flickr
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center | Flickr
New game-changing perspectives about our planet
There's also hope for solving puzzles related to continental drift and plate tectonics in the frozen landscape. Gondwana—the supercontinent that previously comprised Antarctica as well as South America, Africa, Australia, and other landmasses—is of notable interest. There is now a rare opportunity to investigate the geological processes leading to the split of Gondwana and the subsequent spread of continents around the world, and the results could change our current understanding of the Earth's evolution over time.
The results might also have an impact on how we perceive climate change and its possible effects on Antarctica. Scientists can learn more about the stability and susceptibility of polar ice sheets throughout long epochs by investigating the ancient landscape. This information is essential for forecasting Antarctica's future and evaluating the possible effects of global climate change on sea levels.
 U.S. Department of State | Wikimedia Commons
U.S. Department of State | Wikimedia Commons
What's next to come
The task at hand is to safeguard and conserve this precious scientific find. It is hoped that the secrets concealed in Antarctica's frozen layers will continue to be revealed via increased international cooperation and research, and that eventually we will reach a better understanding of the complex geological and climatic workings of our planet.








