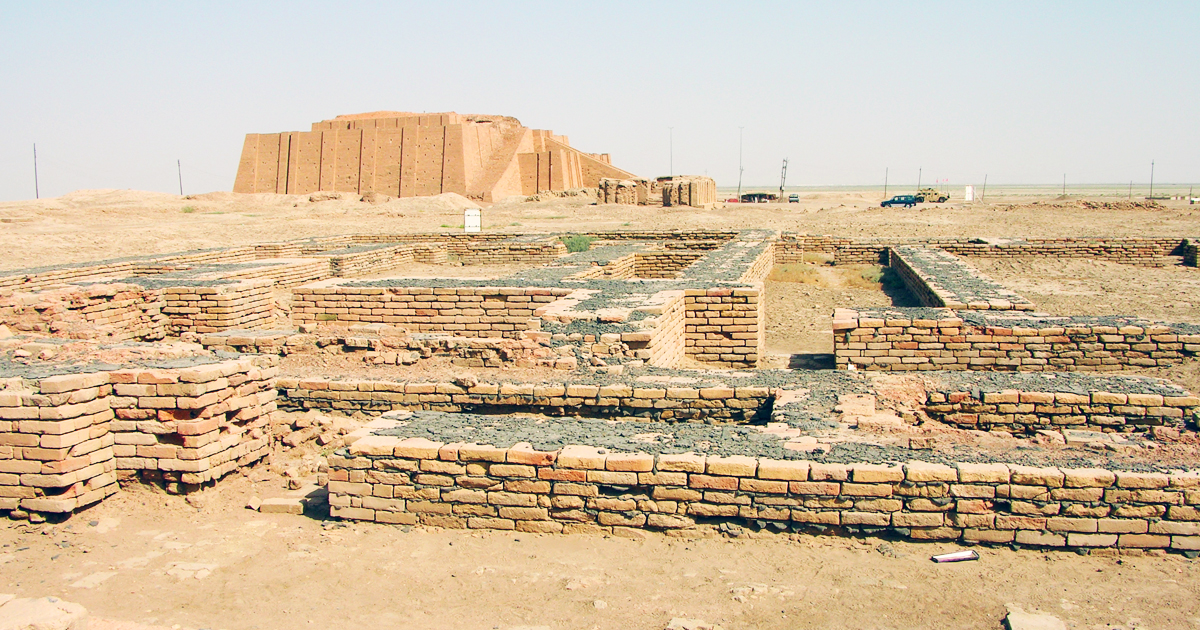
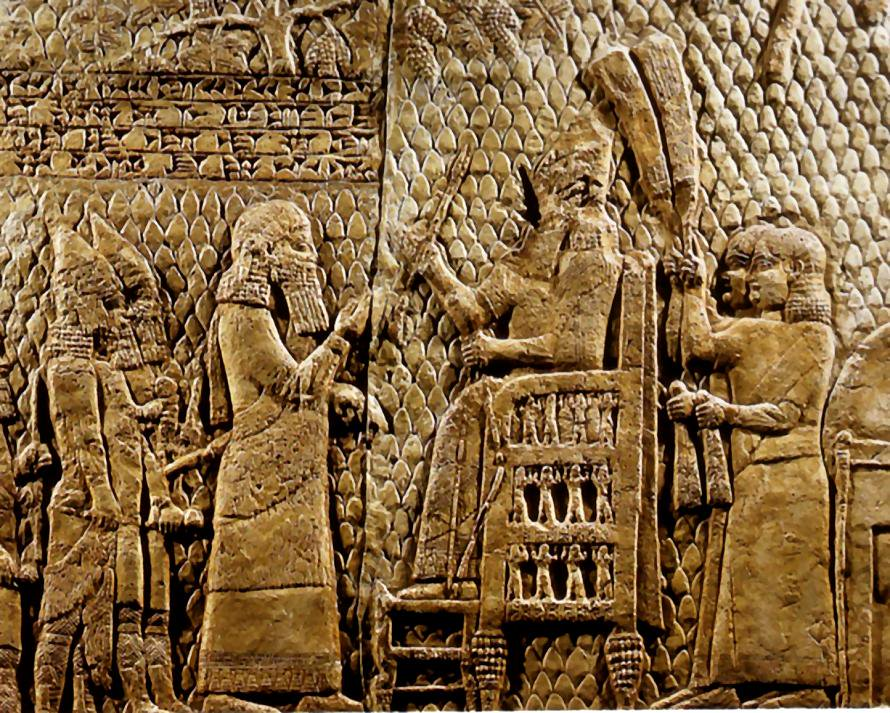
The ancient Sumerians were an advanced people, and traces of their existence are present in Mesopotamia, the birthplace of civilization. The Sumerians, who thrived in what is now southern Iraq, have left a lasting impact on humankind by providing our world with blueprints for technological innovation, complex cultural frameworks, and social order. Even though ancient Sumer vanished from human civilization, their legacy continues to influence fundamental aspects of modern life.
Early beginnings
The Sumerians founded city-states on the fertile grasslands between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers circa 4500 BCE. These city-states, comprising Ur, Uruk, and Lagash, were particularly reputed for their superior urban layouts. Their intricate zeniths and irrigation systems also dominated the region around them.
Perhaps one of the most significant contributions of the Sumerians is cuneiform, the earliest form of writing ever known to mankind. They used wedge-like imprints on clay slabs to create the system, an innovative process that was the first of its kind. The development of this device served as the basis for modern writing systems and set a precedent for management, dialog, and documentation.
 Jacktandy000 | Wikimedia Commons
Jacktandy000 | Wikimedia Commons
A series of firsts for humanity
The Sumerians also adopted a social hierarchy consisting of monarchs, clergymen, and ordinary people. Some of the oldest legal codes, such as the well-known Code of Ur-Nammu and the lesser-known Code of Hammurabi, were incorporated into their government structure. These regulatory structures shaped succeeding legal systems and contributed to the development of concepts like "an eye for an eye," which place a strong emphasis on accountability and justice.
In terms of finance, the Sumerians paved the way for contemporary trade and commerce. Their favorable location at the intersection of major trade routes fostered economic expansion and cross-cultural relations. An important step toward the formation of the present-day monetary system was taken with the creation of the shekel, an early type of currency that enabled trade transactions. The Sumerians exchanged a variety of things, including metals, textiles, and crops with their neighbors.
The original game-changers
The Sumerians were known to be brilliant innovators who developed ground-breaking technologies that still have an impact on today's culture. The wheel and the plow stand out among their many accomplishments as they transformed agriculture and transportation, respectively. Originally utilized for pottery, the wheel eventually found its way onto carts and chariots, allowing for the more efficient transfer of cargo. large-scale farming was made simpler by the plow, which boosted food yields while promoting the proliferation of urban settlements.
The Sumerians also created plenty of art and left behind a rich heritage of culture. Their publications, which address themes of companionship, death, and the human condition, include the Epic of Gilgamesh, one of the first known works of fictional storytelling. Sumerians were also skilled astronomers—they devised the first lunar calendar and set the foundation for future developments in the field of science.
Overall, the Sumerians' innovations in governance, economics, technology, and culture have left an immeasurable impact that permeates our daily lives. The lost civilization of ancient Sumer forever stands as a tribute to the power of human creativity and the lasting influence of a society that created the foundation for modern times.